# 数据结构
# BST树(二叉搜索树)
# 特征
- 每个节点最多有两个子节点
- 每个节点都包含一个Compareable的键
- 每个节点的值都大于左子树任意节点的值
- 每个节点的值都小于右子树任意节点的值
- 所有节点的值都各不相等
- 二叉搜索树可以是一颗空树
# Java代码实现
/**
* @author chenpeng
* @date 2019/5/14
*/
public class BinarySearchTree<K extends Comparable<K>> {
/**
* 插入节点
*
* @param node 二叉树
* @return 新的二叉树
*/
public Node<K> put(Node<K> node, K key) {
if (node == null) {
return new Node<K>(key);
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
node.left = put(node.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
node.right = put(node.right, key);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("repeat data can not add in bst");
}
node.count = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
return node;
}
/**
* 二叉树搜索
*
* @param node 二叉树
* @param key 要搜索的值
* @return 匹配节点,null表示未查询到
*/
public Node<K> get(Node<K> node, K key) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
return get(node.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
return get(node.right, key);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 获取指定节点的子节点总数
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return 节点总数
*/
public int size(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return node.count;
}
/**
* 找到最小节点
*
* @param node 给定二叉树
* @return 最小节点
*/
public Node<K> min(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
return min(node.left);
}
/**
* 删除指定树的最小节点
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return 删除节点后的二叉树
*/
public Node<K> deleteMin(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
node.left = deleteMin(node.left);
node.count = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
return node;
}
/**
* 删除操作(假设n是要被删除的节点)
* 1. n.left==null,删除了 n 节点,n.right就是根节点
* 2. n.rigt==null, 删除了 n 节点, n.left就是根节点
* 3. n.left!=null && n.right!=null ,那么就取 n.right 的最小节点替代被删除的节点,整个树的有序性依然能够保持
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @param key 要删除的key
* @return 删除后的节点
*/
public Node<K> delete(Node<K> node, K key) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
node.left = delete(node.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
node.right = delete(node.right, key);
} else {
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
return null;
}
//左节点为空,直接取右节点作为新节点
if (node.left == null) {
return node.right;
}
//右节点为空,直接取左节点为新节点
if (node.right == null) {
return node.left;
}
Node<K> t = node;
node = min(node.right);
node.right = deleteMin(t.right);
node.left = t.left;
}
node.count = size(node.left) + size(node.right) + 1;
return node;
}
}
class Node<K extends Comparable<?>> {
K key;
Node<K> left;
Node<K> right;
/**
* 节点总量
*/
int count;
public Node(K key) {
this.key = key;
this.count = 1;
}
}
# AVL树(平衡二叉树)
AVL树,也称平衡二叉树,AVL是其发明者Adelson-Velsky and Landis的简写,AVL树属于树的一种,而它也是一个二叉搜索树,不同的是他通过一定机制能够保证二叉树的平衡,平衡的二叉搜索树的查询效率更高。
# 特征
- AVL树是一种二叉搜索树,并且会在插入删除的时候通过旋转达到自平衡
- AVL树拥有二叉搜索树的所有基本特点
- AVL树的每个节点的左右子树的最大高度都不会超过1
- 普通的二叉搜索树查询效率是O(h),h表示二叉树的高度,极端情况下,可能会达到O(n),AVL树的自平衡可以保证其查询效率始终能达到O(Logn)
# AVL树的优势
普通的二叉搜索树的查询效率是O(h),其中h表示二叉树的高度。但是在极端情况下,所有的节点都在树的一边,二叉树退化成了链表,此时二叉树的查询效率就变成了O(n)。AVL树则通过旋转,使得树的高度始终能保持在logn,在牺牲插入性能的条件下达到了提高查询效率的目的。
# 平衡因子
节点N的平衡因子可以通过下面的公式计算出来:BalanceFactory(N) = Height(N.right)-Height(N.left)(也就是左子树的高度-右子树的高度。)
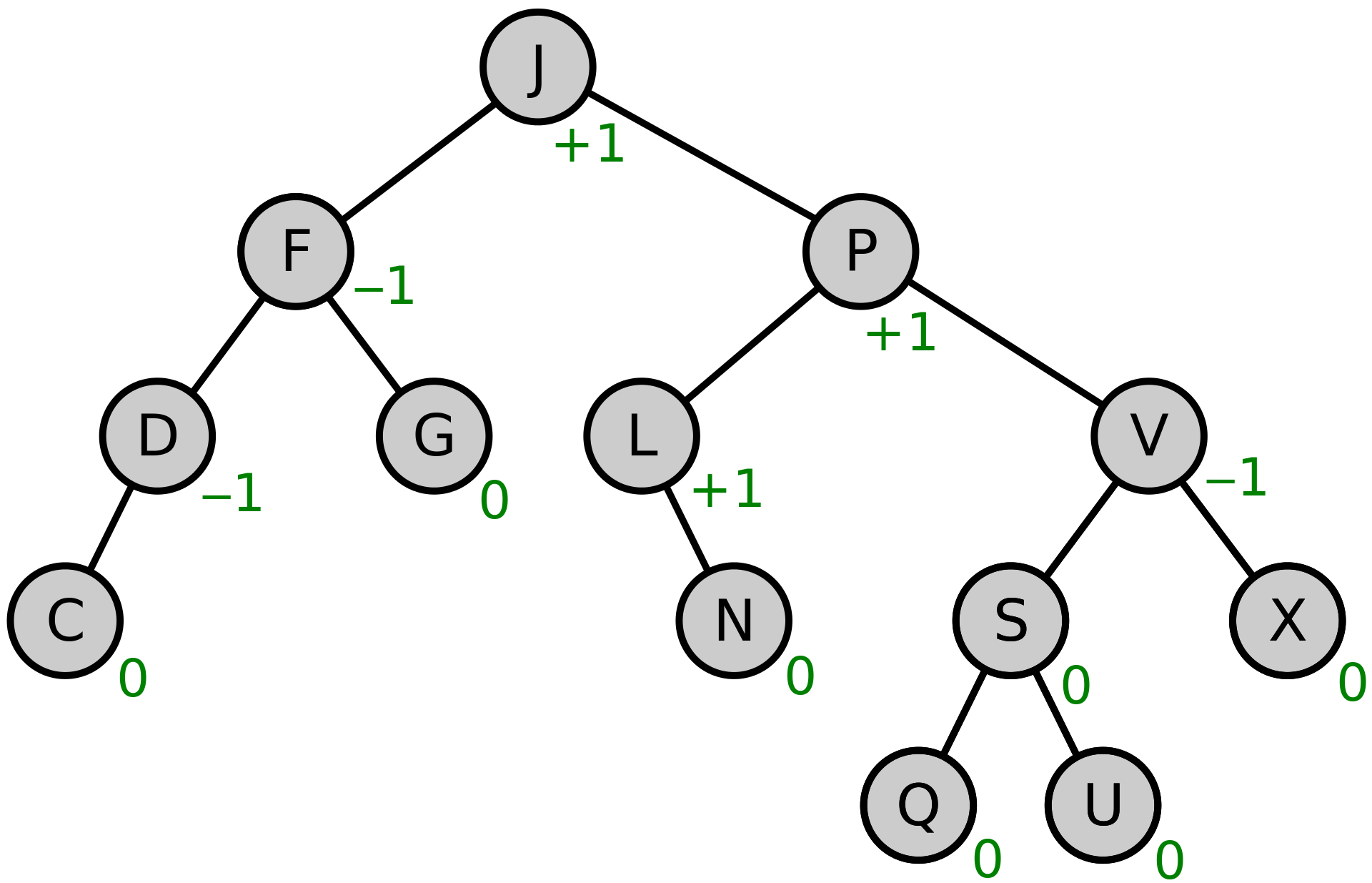
绿色数字表示该节点的平衡因子,只有所有节点的平衡因子在 {-1,0,1} 内, 这棵树才是平衡的。
# 判断树是否平衡
/**
* 节点是否平衡
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return true-平衡 false-不平衡
*/
public boolean isBalanced(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
return Math.abs(height(node.left) - height(node.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(node.left) && isBalanced(node.right);
}
/**
* 计算节点高度
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return 节点高度
*/
public int height(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)) + 1;
}
# AVL树的旋转
- 当插入和删除数据的时候,有可能会破坏树的平衡,这时AVL树会通过旋转的方式来维持整颗树的平衡。
- 旋转只有两种: 左旋和右旋,像左右旋转和右左旋转都是在这个基础上做出来的。
- 每次旋转都要重新计算节点高度,这是判断后续节点是否平衡的重要依据。
# 左旋

/**
* 左旋转
*
* @param x 根节点
* @return 旋转后的根节点
*/
public Node<K> leftRotation(Node<K> x) {
Node<K> y = x.right;
x.right = y.left;
y.left = x;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
return y;
}
# 右旋
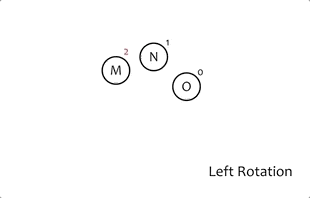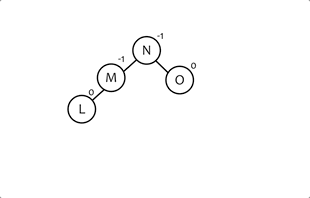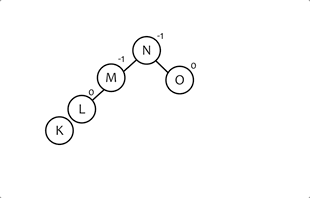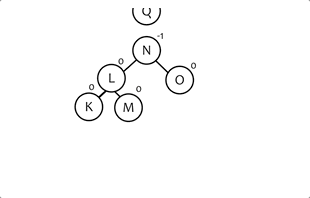
/**
* 右旋转
*
* @param y 根节点
* @return 旋转后的根节点
*/
public Node<K> rightRotation(Node<K> y) {
Node<K> x = y.left;
y.left = x.right;
x.right = y;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
return x;
}
# Java代码实现
public class SelfBalancingBinarySearchTree<K extends Comparable<K>> {
/**
* 左旋转
*
* @param x 根节点
* @return 旋转后的根节点
*/
public Node<K> leftRotation(Node<K> x) {
Node<K> y = x.right;
x.right = y.left;
y.left = x;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
return y;
}
/**
* 右旋转
*
* @param y 根节点
* @return 旋转后的根节点
*/
public Node<K> rightRotation(Node<K> y) {
Node<K> x = y.left;
y.left = x.right;
x.right = y;
y.height = Math.max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1;
x.height = Math.max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1;
return x;
}
public int getBalance(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return height(node.left) - height(node.right);
}
/**
* 插入节点
*
* @param node 二叉树
* @return 新的二叉树
*/
public Node<K> put(Node<K> node, K key) {
if (node == null) {
return new Node<>(key);
}
//1.插入数据
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
node.left = put(node.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
node.right = put(node.right, key);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("duplicate keys not allowed");
}
//2.更新上级节点高度
node.height = 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right));
//3.计算平衡因子,判断平衡是否被破坏
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance <= 1 && balance >= -1) {
return node;
}
//4.平衡被破坏,通过旋转来调整平衡
return reBalance(node);
}
/**
* 二叉树搜索
*
* @param node 二叉树
* @param key 要搜索的值
* @return 匹配节点,null表示未查询到
*/
public Node<K> get(Node<K> node, K key) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
return get(node.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
return get(node.right, key);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 找到最小节点
*
* @param node 给定二叉树
* @return 最小节点
*/
public Node<K> min(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
return min(node.left);
}
/**
* 删除操作(假设n是要被删除的节点)
* 1. n.left==null,删除了 n 节点,n.right就是根节点
* 2. n.rigt==null, 删除了 n 节点, n.left就是根节点
* 3. n.left!=null && n.right!=null ,那么就取 n.right 的最小节点替代被删除的节点,整个树的有序性依然能够保持
* 4. 节点删除后, 判断树有没有失去平衡,如果失去平衡根据删除了左节点还是右节点来判断如何旋转
*
* @param root 给定节点
* @param key 要删除的key
* @return 删除后的节点
*/
public Node<K> delete(Node<K> root, K key) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo(root.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
root.left = delete(root.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
root.right = delete(root.right, key);
} else {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return null;
} else if (root.left == null) {
//左节点为空,直接取右节点作为新节点
root = root.right;
} else if (root.right == null) {
//右节点为空,直接取左节点为新节点
root = root.left;
} else {
//左右节点都不为空
//找到右子树上最小的节点
Node<K> temp = min(root.right);
//将最小节点的值拷贝过来
root.key = temp.key;
//删除最小值
root.right = delete(root.right, temp.key);
}
}
//重新计算高度
root.height = Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
return reBalance(root);
}
/**
* 重新平衡二叉树
*
* @param root 根节点
* @return
*/
public Node<K> reBalance(Node<K> root) {
int balance = getBalance(root);
/**
* 左旋转
* x y
* / \ / \
* y T1 T3 x
* / \ ==> / / \
* T3 T2 T4 T2 T1
* /
* T4
*/
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root.left) >= 0) {
return rightRotation(root);
}
/**
* 左右旋转
* x x T2
* / \ / \ / \
* y T1 T2 T1 y x
* / \ ==> / ==> / \ \
* T3 T2 y T3 T4 T1
* / / \
* T4 T3 T4
*/
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root.left) < 0) {
//对y节点进行左旋
root.left = leftRotation(root.left);
//对x节点进行右旋
return rightRotation(root);
}
/**
* 右旋转
* x y
* / \ / \
* T1 y x T3
* / \ ==> / \ \
* T2 T3 T1 T2 T4
* \
* T4
*/
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root.right) <= 0) {
return leftRotation(root);
}
/**
* 右左旋转
* x x T2
* / \ / \ / \
* T1 y T1 T2 x y
* / \ ==> \ ==> / / \
* T2 T3 y T1 T4 T3
* \ / \
* T4 T4 T3
*/
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root.right) > 0) {
//对y节点进行右旋
root.right = rightRotation(root.right);
//对x节点进行左旋
return leftRotation(root);
}
return root;
}
/**
* 获取节点高度
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return 节点高度
*/
public int height(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return node.height;
}
/**
* 节点是否平衡
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return true-平衡 false-不平衡
*/
public boolean isBalanced(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
return Math.abs(calculateHeight(node.left) - calculateHeight(node.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(node.left) && isBalanced(node.right);
}
/**
* 计算节点高度
*
* @param node 给定节点
* @return 节点高度
*/
public int calculateHeight(Node<K> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(calculateHeight(node.left), calculateHeight(node.right)) + 1;
}
}
public class Node<K extends Comparable<?>> implements Cloneable {
K key;
Node<K> left;
Node<K> right;
/**
* 节点总量
*/
int count;
/**
* 数的高度
*/
int height;
public Node(K key) {
this.key = key;
this.count = 1;
this.height = 1;
}
@Override
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
# 验证程序
public static void main(String... args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; i++) {
list.add((char) i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
//随机打乱顺序
Collections.shuffle(list);
//随机选择插入数量
List<Character> subList = list.subList(0, new Random().nextInt(26) + 1);
//插入删除校验
balanceCheck(subList, null);
System.out.println("balanced: " + subList);
}
System.out.println("all balanced.");
}
public static <K extends Comparable<K>> void balanceCheck(List<K> inputList, List<K> deleteList) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
SelfBalancingBinarySearchTree<K> selfBalancingBinarySearchTree = new SelfBalancingBinarySearchTree<K>();
Node<K> node = null;
for (K key : inputList) {
node = selfBalancingBinarySearchTree.put(node, key);
}
if (!selfBalancingBinarySearchTree.isBalanced(node)) {
System.out.println("输入数据:" + inputList);
BstPrintUtil.printNode(node);
throw new RuntimeException("不平衡");
}
//随机删除多个数据
int total = new Random().nextInt(inputList.size());
if (deleteList == null || deleteList.isEmpty()) {
deleteList = new ArrayList<K>();
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
K toDelete = inputList.get(new Random().nextInt(inputList.size()));
deleteList.add(toDelete);
}
}
Node before;
for (K k : deleteList) {
before = (Node) node.clone();
node = selfBalancingBinarySearchTree.delete(node, k);
//判断删除后是否依然平衡
if (!selfBalancingBinarySearchTree.isBalanced(node)) {
System.out.println("before:");
BstPrintUtil.printNode(before);
System.out.println("inputList:" + inputList);
System.out.println("deleteList:" + deleteList);
System.out.println("删除数据 :" + k);
System.out.println("after:");
BstPrintUtil.printNode(node);
throw new RuntimeException("删除后树不平衡");
}
}
}
public class BstPrintUtil {
/**
* 二维打印树
*
* @param root 给定二叉树
*/
public static void printNode(Node<?> root) {
int maxLevel = BstPrintUtil.maxLevel(root);
List<Node<?>> nodes = new ArrayList<Node<?>>();
nodes.add(root);
printNodeInternal(nodes, 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printNodeInternal(List<Node<?>> nodes, int level, int maxLevel) {
if (nodes.isEmpty() || BstPrintUtil.isAllElementsNull(nodes)) {
return;
}
int floor = maxLevel - level;
int endgeLines = (int) Math.pow(2, (Math.max(floor - 1, 0)));
int firstSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor)) - 1;
int betweenSpaces = (int) Math.pow(2, (floor + 1)) - 1;
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces);
List<Node<?>> newNodes = new ArrayList<Node<?>>();
for (Node<?> node : nodes) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.key);
newNodes.add(node.left);
newNodes.add(node.right);
} else {
newNodes.add(null);
newNodes.add(null);
System.out.print(" ");
}
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(betweenSpaces);
}
System.out.println("");
for (int i = 1; i <= endgeLines; i++) {
for (Node<?> node : nodes) {
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(firstSpaces - i);
if (node == null) {
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(endgeLines + endgeLines + i + 1);
continue;
}
if (node.left != null) {
System.out.print("/");
} else {
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(i + i - 1);
if (node.right != null) {
System.out.print("\\");
} else {
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(1);
}
BstPrintUtil.printWhitespaces(endgeLines + endgeLines - i);
}
System.out.println("");
}
printNodeInternal(newNodes, level + 1, maxLevel);
}
private static void printWhitespaces(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
private static int maxLevel(Node<?> node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
return Math.max(BstPrintUtil.maxLevel(node.left), BstPrintUtil.maxLevel(node.right)) + 1;
}
private static <T> boolean isAllElementsNull(List<T> list) {
for (Object object : list) {
if (object != null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Node<K extends Comparable<?>> {
K key;
Node<K> left;
Node<K> right;
/**
* 节点总量
*/
int count;
public Node(K key) {
this.key = key;
this.count = 1;
}
public static void main(String... args) {
Node<Integer> node = new Node<Integer>(5);
node.left = new Node<Integer>(1);
node.left.right = new Node<Integer>(3);
node.right = new Node<Integer>(7);
node.right.left = new Node<Integer>(6);
node.right.right = new Node<Integer>(8);
BstPrintUtil.printNode(node);
}
}
# 红黑树(特殊的平衡二叉树)
是一种自平衡二叉查找树,1972年由Rudolf Bayer发明,它与AVL树类似,都在插入和删除操作时能通过旋转保持二叉查找树的平衡,以便能获得高效的查找性能。它可以在O(logn)的时间内做查找,插入和删除等操作。红黑树是2-3-4树的一种等同,但有些红黑树设定只能左边是红树,这种情况就是2-3树的一种等同了。对于AVL树来说,红黑树牺牲了部分平衡性以换取插入\删除操作时少量的旋转操作,整体上来说性能要由于AVL。
参考网址:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/e136ec79235c (opens new window)
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1641940303518144126&wfr=spider&for=pc (opens new window)
# 特征
- 节点分为红色或者黑色
- 根节点必为黑色
- 叶子节点都为黑色,且为null。 [注意:这里叶子结点,是指为空(NIL或NULL)的叶子结点!]
- 连接红色节点的两个子节点都为黑色(红黑树不会出现相邻的红色节点)
- 从任意节点出发,到其每个叶子节点的路径中包含相同数量的黑色节点。[确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出俩倍,所以红黑树是相对接近平衡的二叉树的!]
- 新加入到红黑树的节点为红色节点
# B-树(多路搜索树,不一定是二叉的)
1970年,R.Bayer和E.mccreight提出了一种适用于外查找的树,它是一种平衡的多叉树,称为B树(或B-树)
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/wyqwilliam/article/details/82935922 (opens new window)
https://www.e-learn.cn/content/qita/2465295 (opens new window)
# 特征:
# B+树
B+树是应文件系统所需而出的一种B-树的变型树
# 特征
# B*树
是B+树的变体,在B+树的非根和非叶子结点再增加指向兄弟的指针
# 特征
# LSM树(日志结构合并树)
参考:
https://my.oschina.net/u/3768341/blog/1861086 (opens new window)
https://blog.csdn.net/las723/article/details/93767240 (opens new window)
# 对比三种引擎的实现
- Hash存储引擎:哈希表持久化的实现,可以快速支持增删改查等随机操作,且时间复杂度为o(1),但是不支持顺序读取扫描,对应的存储系统为k-v存储系统的实现。
- B+树存储引擎是b树的持久化实现,不仅支持单条记录的增删改查操作,还支持顺序扫描,对应的存储系统就是mysql。
- LSM树存储引擎和b树存储引擎,一样支持,增删改查,也支持顺序扫描操作。LSM牺牲了读性能,提高写性能。
# 核心思路
就是假定内存足够大,因此不需要每次有数据更新就必须将数据写入到磁盘中,而可以先将最新的数据驻留在内存中,等到积累到最后多之后,再使用归并排序的方式将内存内的数据合并追加到磁盘队尾(因为所有待排序的树都是有序的,可以通过合并排序的方式快速合并到一起)。
将对数据的修改增量保存在内存中,达到指定大小限制之后批量把数据flush到磁盘中,磁盘中树定期可以做merge操作,合并成一棵大树,以优化读性能。不过读取的时候稍微麻烦一些,读取时看这些数据在内存中,如果未能命中内存,则需要访问较多的磁盘文件。极端的说,基于LSM树实现的HBase写性能比MySQL高了一个数量级,读性能却低了一个数量级。
# LSM树
理论上,可以是内存中树的一部分和磁盘中第一层树做merge,对于磁盘中的树直接做update操作有可能会破坏物理block的连续性,但是实际应用中,一般lsm有多层,当磁盘中的小树合并成一个大树的时候,可以重新排好顺序,使得block连续,优化读性能。
一般数据库的存储一定要保持有序,有序是一个非常重要的概念(当然hash结构的除外,hash不支持顺序扫描,对应的存储系统为key-value存储系统。对于key-value的插入以及查询,哈希表的复杂度都是O(1),明显比树的操作O(n)快,如果不需要有序的遍历数据,哈希表就是O(1) ).
LSM树相比于B+树(大量的叶节点操作,不仅支持单条记录的增、删、读、改操作,还支持顺序扫描(B+树的叶子节点之间的指针), 对B树的写入过程是一次原位写入的过程,主要分为两个部分,首先是查找到对应的块的位置,然后将新数据写入到刚才查找到的数据块中,然后再查找到块所对应的磁盘物理位置,将数据写入去。当然,在内存比较充足的时候,因为B树的一部分可以被缓存在内存中,所以查找块的过程有一定概率可以在内存内完成,不过为了表述清晰,我们就假定内存很小,只够存一个B树块大小的数据吧。可以看到,在上面的模式中,需要两次随机寻道(一次查找,一次原位写),才能够完成一次数据的写入,代价还是很高的。 ), 弄了很多个小的有序结构,比如每m个数据,在内存里排序一次,下面100个数据,再排序一次……这样依次做下去,我就可以获得N/m个有序的小的有序结构。 在查询的时候,因为不知道这个数据到底是在哪里,所以就从最新的一个小的有序结构里做二分查找,找得到就返回,找不到就继续找下一个小有序结构,一直到找到为止。 很容易可以看出,这样的模式,读取的时间复杂度是(N/m)*log2N 。读取效率是会下降的。
LSM树原理把一棵大树拆分成N棵小树,它首先写入内存中,随着小树越来越大,内存中的小树会flush到磁盘中,磁盘中的树定期可以做merge操作,合并成一棵大树,以优化读性能。
总结为,LSM树并不是像B+树单次在磁盘寻址,根据索引来进行写入。而是大量堆集内存,达到一定阈值后,写入磁盘,因为是批量处理,磁盘IO对其性能影响很小,对写操作的性能大大提升。然后再磁盘内再进行合并(Merge)操作,再来提升读性能,可见,对于即时读取的性能不高,不可能写进去马上就读出来,而是要经过一个Merge的过程。
# 优化
- Bloom filter: 就是个带随即概率的bitmap,可以快速的告诉你,某一个小的有序结构里有没有指定的那个数据的。于是就可以不用二分查找,而只需简单的计算几次就能知道数据是否在某个小集合里啦。效率得到了提升,但付出的是空间代价。
- compact:小树合并为大树:因为小树他性能有问题,所以要有个进程不断地将小树合并到大树上,这样大部分的老数据查询也可以直接使用log2N的方式找到,不需要再进行(N/m)*log2n的查询了。
# 使用LSM树的案例
- rocksDB
- levelDB
- hbase