# 大数据启蒙
# 分治思想1:查找
# 需求
我有一万个元素(比如数字或单词)需要存储
# 如果查找某一个元素是否在这个集合当中,最简单的遍历方式复杂的是多少
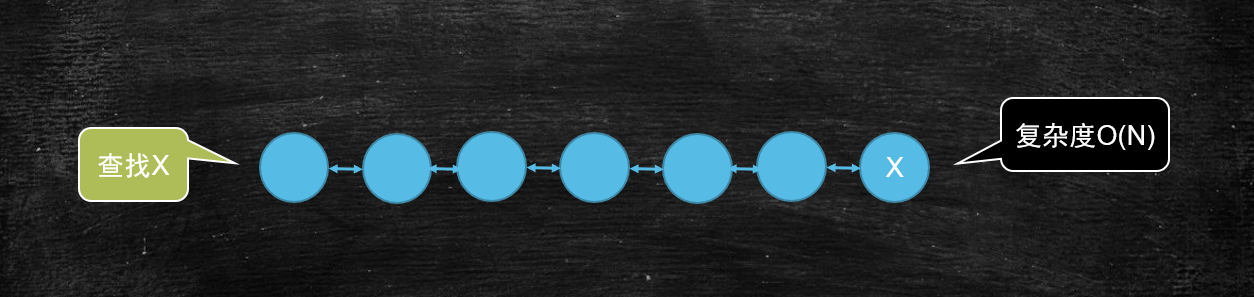
# 如果查找某一个元素是否在这个集合当中,我期望复杂度是O(4)呢
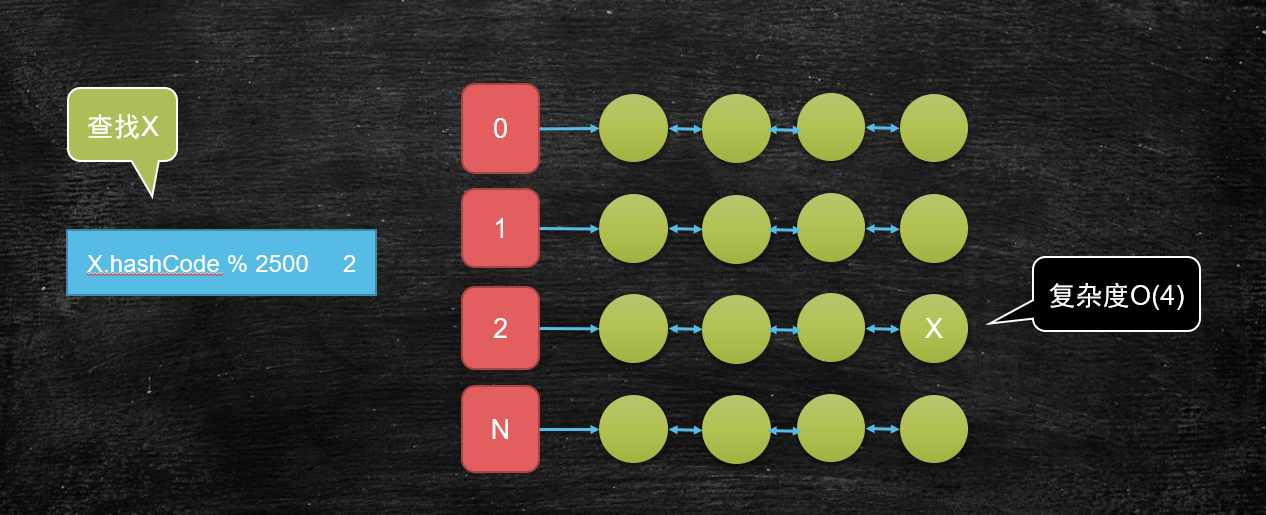
# 分治思想的应用案例
- Redis集群
- ElasticSearch
- Hbase
- HADOOP生态无处不在!
- ......
# 分治思想2:找重复的行
# 需求
有一个非常大的文本文件1T,里面有很多很多的行,只有两行一样,它们出现在未知的位置,需要查找到它们。
假设Io速度是500MB每秒
网络IO速度是100MB每秒
# 单机分治解决
- 单机内存不可能放得下1T的文件,故需要对此文件进行拆解;
- 读取文件,每读一行,求该行的 hashcode 然后%2000,可以把1T的数据分成2000份(每份大小500M),相同的行肯定在同一个文件中;
- 依次遍历2000个文件,找到重复的行。
用时分析:
- 1T文件读取一遍需要约30分钟
- 然后再次遍历2000个小文件,假如重复的行在最后一个文件里,依然需要30分钟
# 集群解决
- 读取文件,每读一行,求该行的 hashcode 然后%2000,可以把1T的数据分成2000份(每份大小500M),相同的行肯定在同一个文件中;
- 把这2000个小文件分发到2000台机器上
- 2000台机器拿到文件后一起进行计算
用时分析:
- 1T文件读取一遍需要约30分钟
- 2000个小文件(1T)分发到2000台机器上需要5个30分钟,也就是两个半小时
- 2000台机器一起执行计算,用时1秒钟
# 分析
- 此时集群的2000台机器还没有1台单机的处理速度快
- 但是:如果考虑每天都有1T的数据产生呢?如果增量了一年,最后一天计算数据呢?
- 第一天的时候,单机需要用1个小时,集群需要用3个小时零1秒
- 第二天的时候,单机需要用2个小时,集群需要用3个小时零2秒(第一天的1T已经分发出去了,只需要分发当天增量的1T数据即可)
- 第三天的时候,单机需要3个小时,集群需要用3个小时零3秒(只需要分发当前增量的1T数据),近似已经追平了
- 第四天的时候,单机需要4个小时,集群需要用3个小时零4秒(只需要分发当前增量的1T数据),已经完胜了
- ......
- 第365天的时候,单机需要365个小时(近半个月),集群需要用3个小时零365秒,完胜。
# 结论
- 分而治之
- 并行计算
- 计算向数据移动(计算找数据)
- 数据本地化读取
# Hadoop
# HDFS
分布式文件系统那么多,为什么hadoop项目还要开发一个hdfs文件系统?
- 分布式存储为了更好的分布式计算
- 一个文件被分成多个相同大小的 block 块,便于同时读取不同的 block 块(计算向数据移动),增加并行度
- 数据的可靠性有保障
- Hdfs支持client给出文件的offset自定义连接哪些block的DN,自定义获取数据
- 支持新增,追加,删除,查询,唯独不支持更新
# 存储模型
- 文件线性按字节切割成块(block),具有offset,id
- 文件与文件的block大小可以不一样
- 一个文件除最后一个block,其他block大小一致
- block的大小依据硬件的I/O特性调整
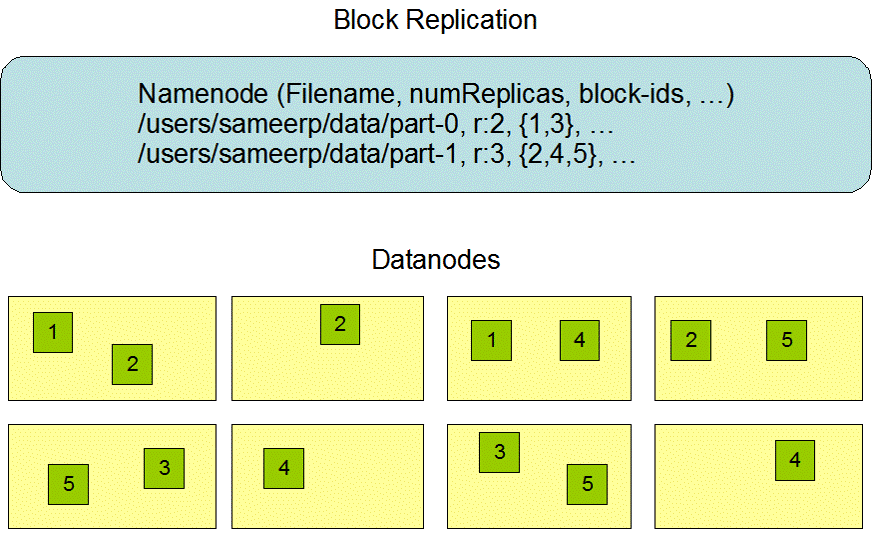
- block被分散存放在集群的节点中,具有location(位置定位信息)
- Block具有副本(replication),没有主从概念,副本不能出现在同一个节点
- 副本是满足可靠性和性能的关键
- 文件上传可以指定block大小和副本数,上传后只能修改副本数
- 一次写入多次读取,不支持修改
- 支持追加数据
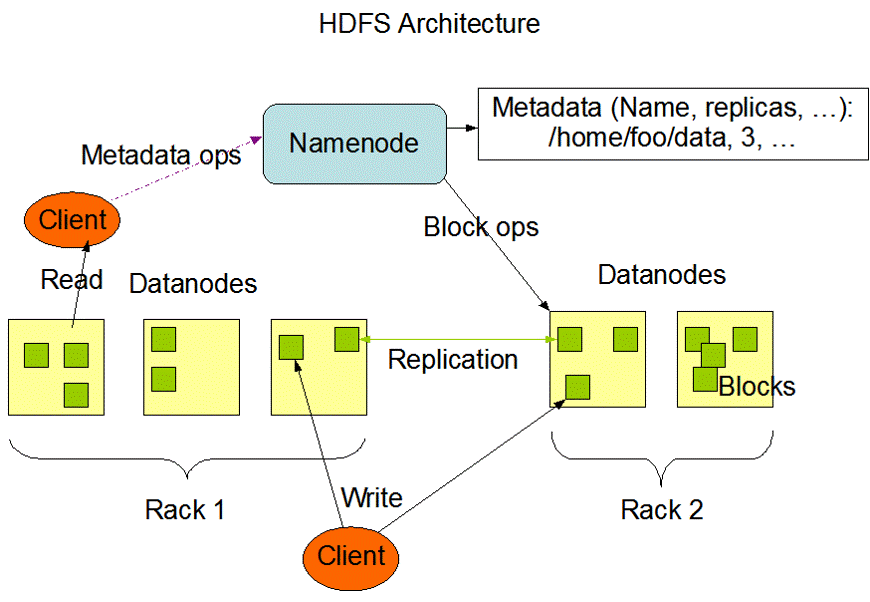
# 架构设计
- HDFS是一个主从(Master/Slaves)架构
- 由一个NameNode和一些DataNode组成
- 面向文件包含:文件数据(data)和文件元数据(metadata)
- NameNode负责存储和管理文件元数据,并维护了一个层次型的文件目录树
- DataNode负责存储文件数据(block块),并提供block的读写
- DataNode与NameNode维持心跳,并汇报自己持有的block信息
- Client和NameNode交互文件元数据和DataNode交互文件block数据
# 角色功能
# NameNode
- 完全基于内存存储文件元数据、目录结构、文件block的映射
- 需要持久化方案保证数据可靠性
- 提供副本放置策略
# DataNode
- 基于本地磁盘存储block(文件的形式)
- 并保存block的校验和数据保证block的可靠性
- 与NameNode保持心跳,汇报block列表状态
# 数据持久化的几种实现方式
# 日志
- 日志文件记录实时发生的增删改操作
- 完成性比较好
- 加载恢复数据慢,占用很大空间
# 镜像
- 间隔(一段时间),内存全量数据基于某一时刻做的向磁盘的溢写
- 如果时间间隔很短的情况下,IO就会很频繁,如果内存数据量大的话,也会很慢
- 因为是间隔的,容易丢失一部分数据
# 元数据持久化
数据持久化方式:日志(EditLog) + 镜像(FsImage)
- 任何对文件系统元数据产生修改的操作,Namenode都会使用一种称为EditLog的事务日志记录下来
- 使用FsImage存储内存所有的元数据状态
- 使用本地磁盘保存EditLog和FsImage
- EditLog具有完整性,数据丢失少,但恢复速度慢,并有体积膨胀风险
- FsImage具有恢复速度快,体积与内存数据相当,但不能实时保存,数据丢失多
- NameNode使用了FsImage+EditLog整合的方案:
- 滚动将增量的EditLog更新到FsImage,以保证更近时点的FsImage和更小的EditLog体积
- 在持久化EditLog的时候,文件的属性信息会进行持久化,块的元数据不会进行持久化。等待datanode来汇报。
cd ./local/dfs/name/current # 观察 editlog的id是不是再fsimage的后边 cd ./local/dfs/secondary/current # SNN 只需要从NN拷贝最后时点的FSimage和增量的Editlog cd ./local/dfs/data/current/BP-281147636-192.168.150.11-1560691854170/current/finalized/subdir0/subdir0 # 检查data.txt被切割的块,他们数据什么样子
# 安全模式
- HDFS搭建时会格式化,格式化操作会产生一个空的FsImage
- 当Namenode启动时,它从硬盘中读取Editlog和FsImage
- 将所有Editlog中的事务作用在内存中的FsImage上
- 并将这个新版本的FsImage从内存中保存到本地磁盘上
- 然后删除旧的Editlog,因为这个旧的Editlog的事务都已经作用在FsImage上了,所以此时的FsImage已经是最新的全量数据了
- Namenode启动后会进入一个称为安全模式的特殊状态。
- 处于安全模式的Namenode是不会进行数据块的复制的。
- Namenode从所有的 Datanode接收心跳信号和块状态报告。
- 每当Namenode检测确认某个数据块的副本数目达到这个最小值,那么该数据块就会被认为是副本安全(safely replicated)的。
- 在一定百分比(这个参数可配置)的数据块被Namenode检测确认是安全之后(如果有些datanode一直起不起来,加上一个额外的30秒等待时间),Namenode将退出安全模式状态。
- 接下来它会确定还有哪些数据块的副本没有达到指定数目,并将这些数据块复制到其他Datanode上。
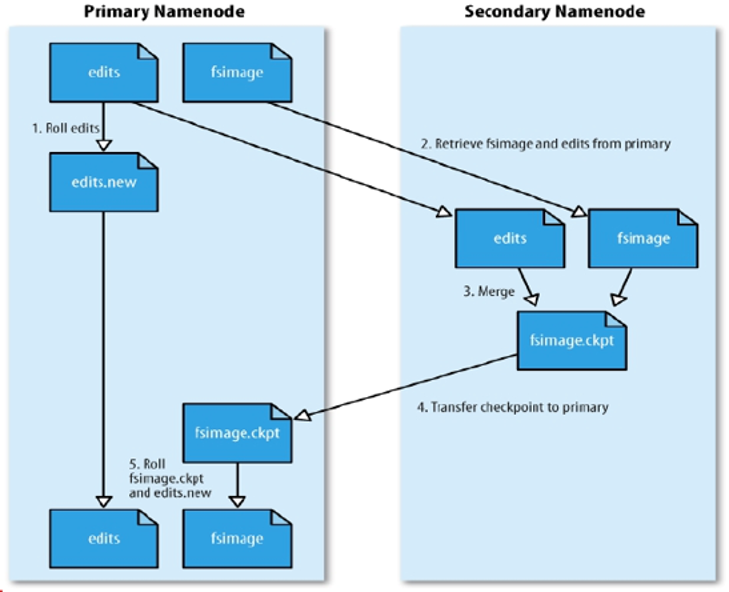
# HDFS中的SNN
SecondaryNameNode(SNN)
- 在非Ha模式下,SNN一般是独立的节点,周期完成对NN的EditLog向FsImage合并,减少EditLog大小,减少NN启动时间
- 根据配置文件设置的时间间隔fs.checkpoint.period 默认3600秒
- 根据配置文件设置edits log大小 fs.checkpoint.size 规定edits文件的最大值默认是64MB
# Block的副本放置策略
1.x的时候,第二个副本和第一个副本在同一个机架,第三个副本才会出机架
2.x的时候,第二个副本就已经出机架了,第三个副本和第二个副本同一个机架,(第三个副本和第二个副本在同一机架,可以减少网络IO)
- 第一个副本:放置在上传文件的DN;如果是集群外提交,则随机挑选一台磁盘不太满,CPU不太忙的节点。
- 第二个副本:放置在于第一个副本不同的 机架的节点上。
- 第三个副本:与第二个副本相同机架的节点。
- 更多副本:随机节点。
# HDFS写流程
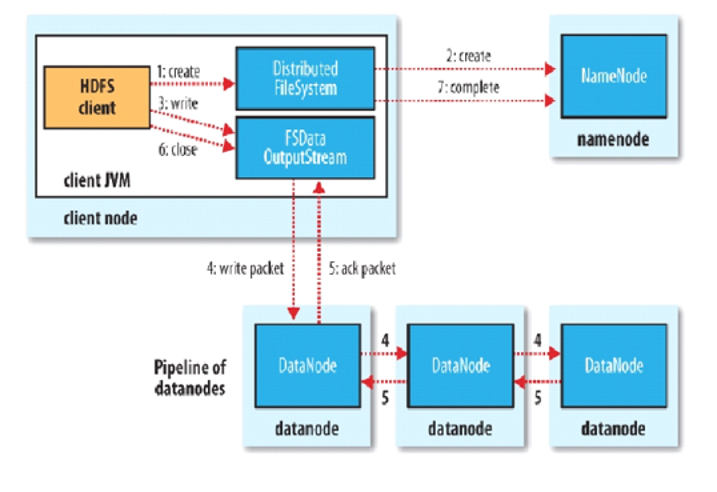
- Client和NN连接创建文件元数据
- NN判定元数据是否有效(是否已经存在,是否有权限)
- NN触发副本放置策略,返回一个有序的DN列表
- Client和DN建立Pipeline连接(小字节传输,支持最大力度的并行,类似流水线)
- Client将块切分成packet(64KB),并使用chunk数据的字节(512B)+chucksum校验盒(4B)填充
- Client将packet放入发送队列dataqueue中,并向第一个DN发送
- 第一个DN收到packet后本地保存并发送给第二个DN
- 第二个DN收到packet后本地保存并发送给第三个DN
- 这一个过程中,上游节点同时发送下一个packet
- 生活中类比工厂的流水线:结论:流式其实也是变种的并行计算
- Hdfs使用这种传输方式,副本数对于client是透明的
- 当block传输完成,DN们各自向NN汇报,同时client继续传输下一个block
- 所以,client的传输和block的汇报也是并行的
如果中间有datanode挂掉了,则直接跳过该datanode往后传输,等传输完成之后,datanode会给namenode汇报block信息,如果和副本数量不一致,则namenode会触发副本放置策略。
# HDFS读流程
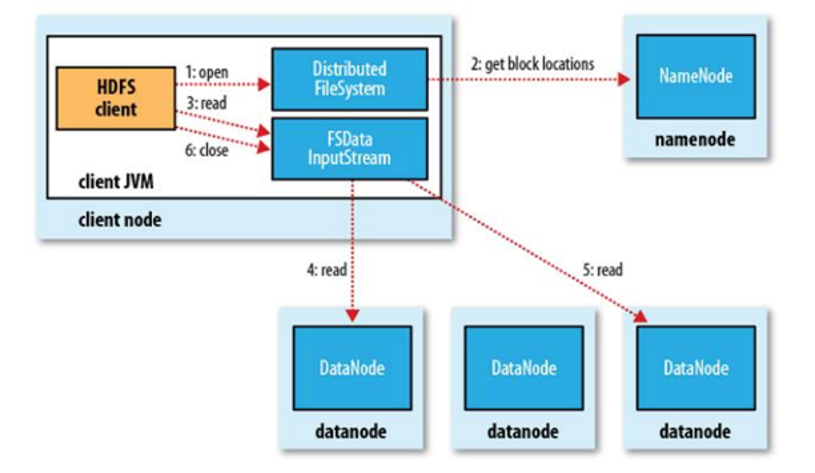
- 为了降低整体的带宽消耗和读取延时,HDFS会尽量让读取程序读取离它最近的副本。
- 如果在读取程序的同一个机架上有一个副本,那么就读取该副本。
- 如果一个HDFS集群跨越多个数据中心,那么客户端也将首先读本地数据中心的副本。
- 语义:下载一个文件:
- Client和NN交互文件元数据获取fileBlockLocation
- NN会按距离策略排序返回
- Client尝试下载block并校验数据完整性
- 语义:下载一个文件其实是获取文件的所有的block元数据,那么子集获取某些block应该成立
- Hdfs支持client给出文件的offset自定义连接哪些block的DN,自定义获取数据
- 这个是支持计算层的分治、并行计算的核心
# API
# 环境权限
1)参考系统登录用户名;登陆用户名改为root
2)参考环境变量;HADOOP_USER_NAME=root
3)代码中给出;System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root");
# 初始化依赖环境
private FileSystem fs = null;
public Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
@Before
public void before() throws Exception {
URI url = new URI("hdfs://mycluster");
fs = FileSystem.get(url, conf, "root");
}
# 创建hdfs目录
@Test
public void mkdir() throws Exception {
Path path = new Path("/user/root");
if (fs.exists(path)) {
fs.delete(path, true);
}
fs.mkdirs(path);
}
# 上传文件
@Test
public void upload() throws Exception {
Path remoteFilePath = new Path("hdfs路径");
if (fs.exists(remoteFilePath)) {
fs.delete(remoteFilePath, true);
}
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("本地文件地址"));
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);
FSDataOutputStream outputStream = fs.create(remoteFilePath);
IOUtils.copyBytes(bufferedInputStream, outputStream, conf, true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (bufferedInputStream != null) {
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
}
# 获取文件块信息
@Test
public void getFileBlock() throws Exception {
Path remoteFilePath = new Path("hdfs文件路径");
FileStatus fileStatus = fs.getFileStatus(remoteFilePath);
BlockLocation[] blockLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(fileStatus, 0, fileStatus.getLen());
for (BlockLocation blockLocation : blockLocations) {
System.out.println(blockLocation);
}
}
# MapReduce
# Map映射
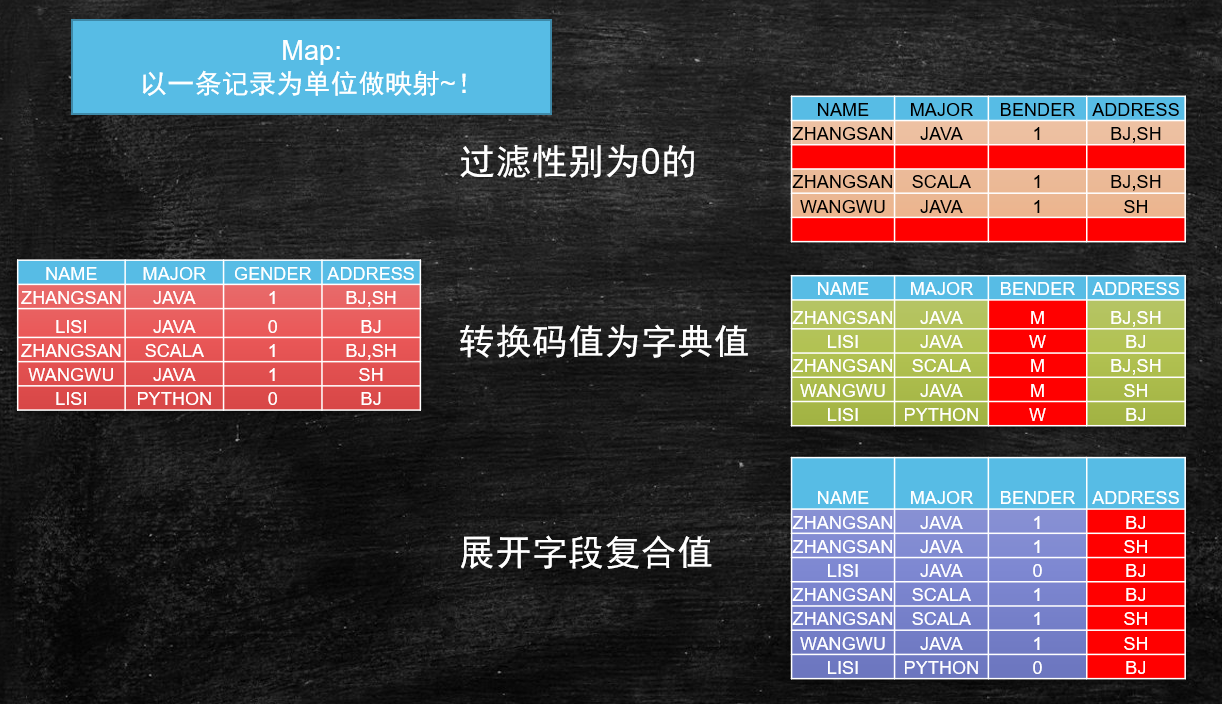
以上三种操作,在进行计算时,是以一条记录为单位,不会关心其他记录的,这种转换的过程就叫做映射 Map
- 过滤
- 转换
- 一变多
# Reduce分组计算
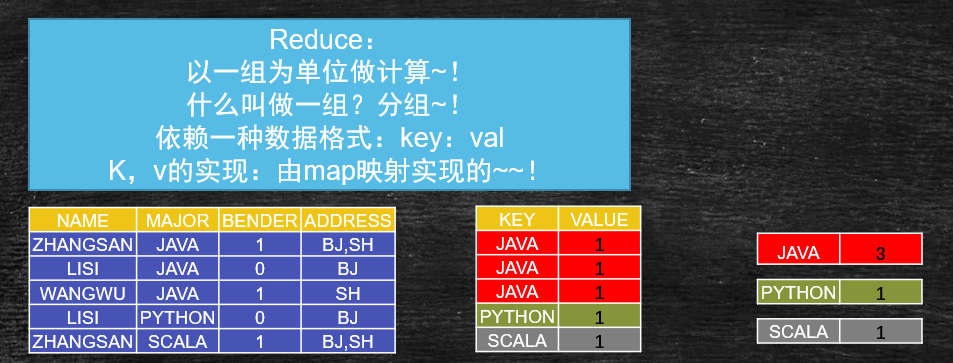
以一组为单位的计算时,叫做分组,分组必须要有一个key值,也就是kv的实现。
# MapReduce
- Map
- 映射、变换、过滤
- 1进N出
- Reduce
- 分解、缩小、归纳
- 一组进N出
- (KEY,VAL)
- 键值对的键划分数据分组
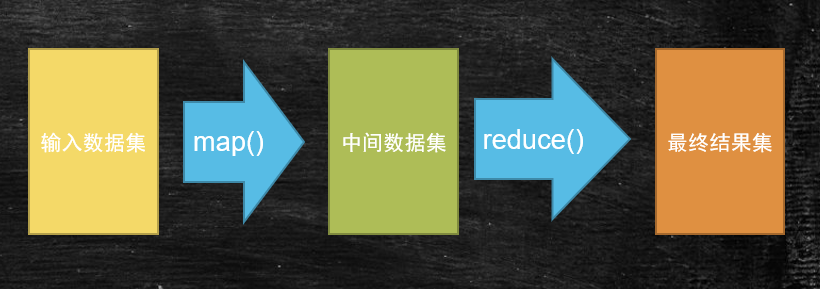
# MapReduce详细的计算过程
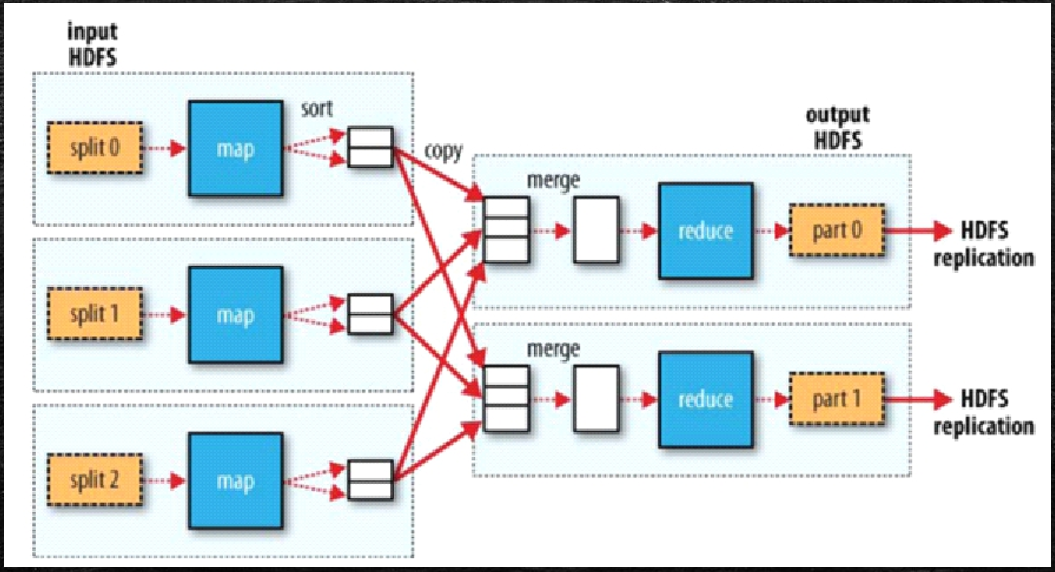
数据以一条记录为单位经过Map方法映射成KV,相同的key为一组,这一组数据调用一次Reduce方法,在方法内迭代计算这一组的数据。
一个 split(切片)对应一个Map任务
一个文件在HDFS中会根据blockSize切成N多个块
默认情况下,一个 split(切片)对应一个block块
加入 split(切片)的概念是为了和block块解耦,可以支持动态调整切片大小
所有的Map执行完成之后,才能进行Reduce环节执行(线性依赖关系)
有几个Reduce,就可以按照key的hash模上几,拉取到不同的Reduce进程里(Reduce中组是不能再分的)
Map的并行度有split(切片)来决定,Reduce的并行度(默认一个)有人来决定
一个Reduce执行的任务交一个分区
比例关系:
- block > split
- 1:1(默认)
- N:1
- 1:N(CPU密集型)
- split > map
- 1:1
- map > reduce
- N:1(默认)
- N:N(人为指定多个Reduce,同一个组不能被打散到不同的 partition(分区,task任务,一个Reduce任务)里)
- 1:1
- 1:N(人为指定map为1个,多个reduce处理不同的组)
- group(key) > partition
- 1:1(一个组去到一个partition)
- N:1(一个partition(task任务,Reduce任务)处理所有的组)
- N:N
# MapReduce详细拆解过程
迭代器模式是批量计算中非常优美的实现形!!!
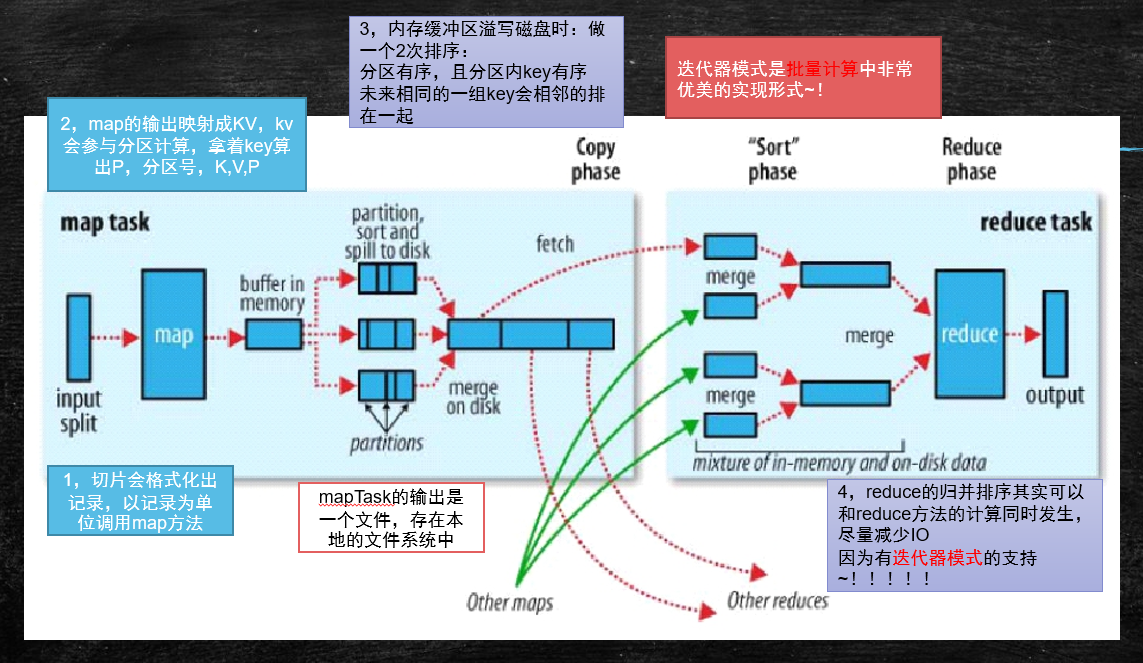
- 切片会格式化出记录,以记录为单位调用map方法
- map的输出映射成KV,kv会参与分区计算,拿着key算出P,分区号,K,V,P
- 内存缓冲区溢写磁盘时:做一个2次排序:分区有序,且分区内key有序;未来相同的一组key会相邻的排在一起
- 如果此时不做排序,当执行Reduce时,每一个Reduce都要全量遍历该文件,增大磁盘IO
- 当内存缓存区溢写磁盘时,进行一次排序(内存比磁盘快了10万倍,在内存中排序不影响性能,缓冲区有大小限制,不会特别大)
- reduce的归并排序其实可以和reduce方法的计算同时发生,尽量减少IO。因为有迭代器模式的支持!!!
# 计算向数据移动
HDFS肯定会暴露block块的位置
- DataNode负责管理Block
- TaskTracker一般会和DataNode部署在一起,主要负责任务的执行
最终计算向数据移动的实现:代码在某一个节点被启动,通过cli上传,TaskTracker下载,并启动相应的任务
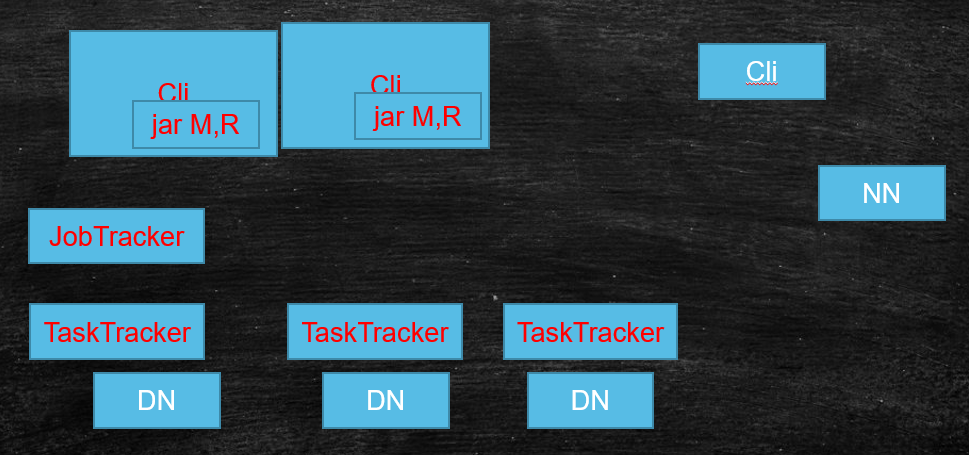
# Client
- 有执行逻辑(MR)
- 会根据每次的计算数据,咨询NameNode获取元数据的Block信息(offset,locations),并计算split(切片),最终得到一个切片的清单(包含:split的偏移量,以及对应的map任务应该移动到哪些节点 locations )
- 生成计算程序未来运行时的相关配置文件
- 未来的移动应该相对可靠:client会将jar,split清单,配置文件,上传到HDFS的目录中,此时的副本默认数是10
- 调用JobTracker,通知要启动一个计算程序了,并且告诉文件放在了HDFS的哪些地方
# JobTracker
作用
- 资源管理
- 任务调度
存在的问题
单点故障
压力过大
集成了资源管理和任务调度,两者耦合
未来新的计算框架不能复用资源管理
- 重复造轮子
- 因为各自实现资源管理,但是他们不熟在同一批硬件上,因为隔离,所以不能感知对方的使用,会造成资源争抢
执行流程:
- 从HDFS中取回split清单
- 根据自己收到的TaskTracker汇报的资源,最终确定每一个split对应的map应该去到哪一个节点,得到一个确定的清单
- 未来TaskTracker在做心跳的时候,会取回分配给自己的任务信息
# TaskTracker
- 任务管理
- 资源汇报
执行流程:
- 在心跳取回任务信息
- 从HDFS中下载jar和相关配置文件到本地
- 最终启动任务描述中的Map/Reduce
# Yarn:资源管理
# 架构图
- MR-cli (切片清单 / 配置 / jar / 上传到HDFS)
- 访问RM申请AppMaster
- RM选择一台不忙的节点通知NM启动一个Container,在里面反射生成一个MRAppMaster
- 启动MRAppMaster,从HDFS上下载切片清单,向RM申请资源
- RM根据自己掌握的资源情况得到一个确定的清单,通知NM来启动container
- container启动后会反向注册到已经启动的MRAppMaster进程
- MRAppMaster(更像曾经的JobTracker阉割版(不带资源管理))最终会将任务Task发送给container(消息)
- container会反射相应的Task类为对象,调用方法执行,其结果就是执行我们的业务逻辑代码
- 计算框架都有Task失败重试的机制。
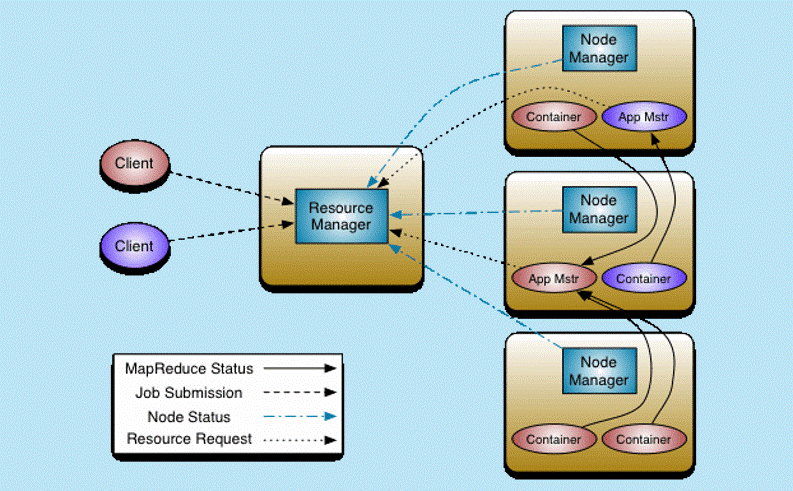
结论:
- 单点故障
- 曾经是全局的,JobTracker如果挂了,整个计算层没有了调度
- yarn:每一个app都有一个自己的AppMaster调度,AppMaster支持失败重试
- 压力过大
- yarn中每个计算程序自由AppMaster,每个AppMaster只负责自己计算程序的任务调度,AppMaster是在不同的节点中启动的,默认有了负载的光环
- 集成了资源管理和任务调度,两者耦合
- 因为yarn只是资源管理,不负责具体的任务调度;只要计算框架继承了yarn的AppMaster,大家都可以使用一个统一视图的资源层。
# 模型
# ResourceManager
ResourceManager支持HA模式
作用:
- 与客户端进行交互,处理来自于客户端的请求,如查询应用的运行情况等。
- 启动和管理各个应用的ApplicationMaster,并且为ApplicationMaster申请第一个Container用于启动和在它运行失败时将它重新启动。
- 管理NodeManager,接收来自NodeManager的资源和节点健康情况汇报,并向NodeManager下达管理资源命令,例如kill掉某个container。
- 资源管理和调度,接收来自ApplicationMaster的资源申请,并且为其进行分配。这个是它的最重要的职能。
# NodeManager
作用:
- NodeManager通过ResourceTrackerProtocol协议向RM注册,汇报节点的健康状态以及Container的运行状态,并领取RM下发的命令例如重新初始化Container,清理Container等;在这个协议中NodeManager主动向RM发请求,RM响应NodeManager的请求。
- 应用程序的ApplicationMaster通过ContainerManagementProtocol协议与NodeManager通信发起针对Container的命令操作,例如:启动,杀死Container,获取Container的运行状态等;在该协议中ApplicationMaster主动向NodeManager发送请求,NodeManager接收到请求做出响应。
# ApplicationMaster
ApplicationMaster实际上是特定计算框架的一个实例,每种计算框架都有自己独特的ApplicationMaster,负责与ResourceManager协商资源,并和NodeManager协同来执行和监控Container。MapReduce只是可以运行在YARN上一种计算框架。
作用:
- 初始化向ResourceManager报告自己的活跃信息的进程
- 计算应用程序的的资源需求。
- 静态资源:在任务提交时就能确定,并且在AM运行时不再变化的资源,比如MapReduce程序中的Map的数量
- 动态资源: AM在运行时确定要请求数量的资源是动态资源。
- 将需求转换为YARN调度器可以理解的ResourceRequest,与调度器协商申请资源
- 与NodeManager协同合作使用分配的Container
- 跟踪正在运行的Container状态,监控它的运行。
- 对Container或者节点失败的情况进行处理,在必要的情况下重新申请资源。
# container
可以让JVM进程在上面运行;被NodeManager监控资源使用情况,如果发现有超额,NodeManager直接把该进程 kill 掉;使用 cgroup 内核级技术,在启动JVM进程时,由Kernel 约束死使用的资源。
- 是集群中单个节点上的一组资源(内存,CPU,归属于哪个NM),由NM监控,由RM调度
- 接收ApplicationMaster的任务启动命令
- 主动拉取HDFS上的jar和相关的配置,作为任务运行环境
# 总结
- 1.x 中 JobTracker、TaskTracker是常服务。
- 2.x 只有没有了这些服务;相对的,MR的cli、【调度】、【任务】,这些都是临时的服务了。
# Client源码分析
没有计算发生 很重要:支撑了计算向数据移动和计算的并行度 1,Checking the input and output specifications of the job. 2,Computing the InputSplits for the job. // split ->并行度和计算向数据移动就可以实现了 3,Setup the requisite accounting information for the DistributedCache of the job, if necessary. 4,Copying the job's jar and configuration to the map-reduce system directory on the distributed file-system. 5,Submitting the job to the JobTracker and optionally monitoring it's status MR框架默认的输入格式化类: TextInputFormat < FileInputFormat < InputFormat getSplits() minSize = 1 maxSize = Long.Max blockSize = file splitSize = Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); //默认split大小等于block大小 切片split是一个窗口机制:(调大split改小,调小split改大) 如果我想得到一个比block大的split: if ((blkLocations[i].getOffset() <= offset < blkLocations[i].getOffset() + blkLocations[i].getLength())) split:解耦 存储层和计算层 1,file 2,offset 3,length 4,hosts //支撑的计算向数据移动
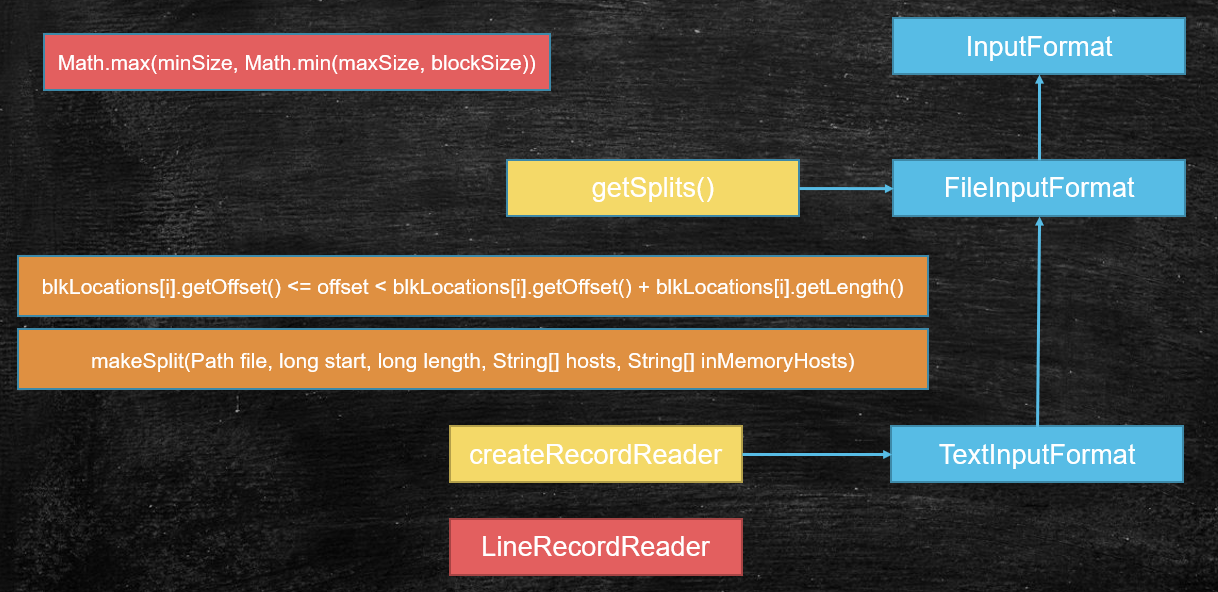
# 默认输入格式化类
// 输入格式化类,默认为TextInputFormat.class
// 可以通过以下几种方式进行干预
// 1. job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
# 计算切片
/**
* Generate the list of files and make them into FileSplits.
* @param job the job context
* @throws IOException
*/
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
// 默认值:1,
// 可以通过以下几种方式进行干预
// 1. TextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 111);
// 2. conf.set(FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MINSIZE, "111");
// 3. 也可以通过运行主方法时外部传参
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
// 默认值:Long.MAX_VALUE
// 可以通过以下几种方式进行干预
// 1. TextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 111);
// 2. conf.set(FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MAXSIZE, "111");
// 3. 也可以通过运行主方法时外部传参
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
// generate splits
List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
// 获取当前job计算需要的所有文件的状态列表
List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job);
for (FileStatus file: files) {
Path path = file.getPath();
long length = file.getLen();
if (length != 0) {
// 每一个文件所有的block块信息
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
// 是否可以做切片,分布式文件可以做切片
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
// 块文件大小
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
// 计算切片大小:splitSize = Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
// minSize默认是1,maxSize默认事Long.MAX_VALUE
// block只要有内容,blockSize肯定大于1,故默认 splitSize = blockSize
// 切片 split 是一个窗口机制(调大split改小值,调小split改大值)
// 如果我想得到一个比block大的split,
// 人为干预 minSize 的大小,只要比 blockSize 大即可
// 如果我想得到一个比block小的split,
// 人为干预 maxSize 的大小,只要比 blockSize 小即可
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
// 找到每一个切片对应的块的偏移量的算法
// 切片最重要的四个属性:1.file;2.offset;3.length;4.hosts//支持计算向数据移动
// blkLocations[i].getOffset() <= offset < blkLocations[i].getOffset() + blkLocations[i].getLength()
long bytesRemaining = length;
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
// 处理最后一个block块
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
}
// 经过上面的算法实例demo
// 文件大小:100
// 块大小: 10
// 切片大小:15
// offset,splitSize, blockIndex
// 0,15 0
// 15,15 1
// 30,15 3
// 45,15 4
// 60,15 6
// 75,15 7
// 90,10, 9
} else { // not splitable
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts(),
blkLocations[0].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else {
//Create empty hosts array for zero length files
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
}
}
// Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen
job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
sw.stop();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
+ ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
return splits;
}
# 上传切片清单和配置
List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job);
T[] array = (T[]) splits.toArray(new InputSplit[splits.size()]);
// sort the splits into order based on size, so that the biggest
// go first
Arrays.sort(array, new SplitComparator());
// 切片清单和配置写入hdfs
JobSplitWriter.createSplitFiles(jobSubmitDir, conf,
jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(conf), array);
# MapTask源码分析
input -> map -> output input:(split+format) 通用的知识,未来的spark底层也是 来自于我们的输入格式化类给我们实际返回的记录读取器对象 TextInputFormat->LineRecordreader split: file , offset , length init(): in = fs.open(file).seek(offset) 除了第一个切片对应的map,之后的map都在init环节, 从切片包含的数据中,让出第一行,并把切片的起始更新为切片的第二行。 换言之,前一个map会多读取一行,来弥补hdfs把数据切割的问题~! nextKeyValue(): 1,读取数据中的一条记录对key,value赋值 2,返回布尔值 getCurrentKey(): getCurrentValue(): output: NewOutputCollector partitioner collector MapOutputBuffer: *: map输出的KV会序列化成字节数组,算出P,最中是3元组:K,V,P buffer是使用的环形缓冲区: 1,本质还是线性字节数组 2,赤道,两端方向放KV,索引 3,索引:是固定宽度:16B:4个int a)Partition 分区号 b)Key Start key的起始位置 c)Value Start value的起始位置 d)Value Length value的长度 5,如果数据填充到阈值:80%,启动线程: 快速排序80%数据,同时map输出的线程向剩余的空间写 快速排序的过程:是比较key排序,但是移动的是索引 6,最终,溢写时只要按照排序的索引,卸下的文件中的数据就是有序的 注意:排序是二次排序(索引里有P,排序先比较索引的P决定顺序,然后在比较相同P中的Key的顺序) 分区有序 : 最后reduce拉取是按照分区的 分区内key有序: 因为reduce计算是按分组计算,分组的语义(相同的key排在了一起) 7,调优:combiner 1,其实就是一个map里的reduce 按组统计 2,发生在哪个时间点: a)内存溢写数据之前排序之后 溢写的io变少~! b)最终map输出结束,过程中,buffer溢写出多个小文件(内部有序) minSpillsForCombine = 3(当溢写次数超过了这个值,会触发合并的combiner) map最终会把溢写出来的小文件合并成一个大文件: 避免小文件的碎片化对未来reduce拉取数据造成的随机读写 也会触发combine 3,combine注意 必须幂等 例子: 1,求和计算 1,平均数计算 80:数值和,个数和 init(): spillper = 0.8 sortmb = 100M sorter = QuickSort comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator(); 1,优先取用户覆盖的自定义排序比较器 2,保底,取key这个类型自身的比较器 combiner ?reduce minSpillsForCombine = 3 SpillThread sortAndSpill() if (combinerRunner == null)
# Map主要流程:MapTask.run();
try {
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
// 调用map的run方法
mapper.run(mapperContext);
// 计算完成
mapPhase.complete();
// 执行排序
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT);
// 状态更新
statusUpdate(umbilical);
// 关闭输入流
input.close();
input = null;
// 关闭输出流
output.close(mapperContext);
output = null;
} finally {
closeQuietly(input);
closeQuietly(output, mapperContext);
}
# 前置参数组装:MapTask.runNewMapper();
// make a task context so we can get the classes
// 构造一个任务的上下文对象,方便在后续的处理逻辑中拿到相关的配置
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper
// 根据指定的 MapperClass 类反射出对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format
// 根据指定的或者默认的输入格式化类,反射出具体的输入对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split
// 根据当前map获取要读取文件块的切片(此时计算已经移动到对应的节点上了)
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);
// 构造一个记录读取器:把切片和输入格式化类传了进去,就意味着,这个类可以读取指定偏移位置的数据了
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
// get an output object
// 构造输出格式化类
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
// 引用!!!Map输出的处理:创建分区器!!!
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
// 包装 MapContext 的上下文对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
// 再包装 Mapper 的上下文对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);
# Map的run方法
/**
* Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the
* execution of the Mapper.
* @param context
* @throws IOException
*/
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
// 这个context里面包装了很多层对象,最重要的是包装了 记录读取器以及切片
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
# RecordReader初始化对于切割字符串的处理
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
// 先拿到切片
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 拿到切片的起始位置(也就是offset)
start = split.getStart();
// 计算切片的终止位置
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split(打开文件系统,并seek到切片的起始位置)
// 拿到分布式文件系统的文件对象
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
// 打开要读取的文件(面向文件的输入流)
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
if (start != 0) {
// So we have a split that is only part of a file stored using
// a Compression codec that cannot be split.
throw new IOException("Cannot seek in " +
codec.getClass().getSimpleName() + " compressed stream");
}
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
// seek到自己要读的切片的起始位置
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
if (start != 0) {
// 非第一个block块,读取第一行数据丢弃,更改偏移量的起始(从第二行开始)
// 意味着每一个map都会读取下一个block块的第一行数据
// 或多或少都会有一部分数据移动的过程,但这个数据不是全量,只是一部分,总的来说要比单机快很多
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}
# RecordReader的nextKeyValue方法
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
// map任务第一次进来,key为空,创建一个LongWritable对象,()
key = new LongWritable();
}
// 设置起始偏移量
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
// 读出一行,value的引用指向了行记录,
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
// 更改起始位置偏移量,因为这一行已经读过了
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
// 只要能够拿到行大小(newSize),就返回true,同时给key,value进行赋值
if (newSize == 0) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
@Override
public LongWritable getCurrentKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentValue() {
return value;
}
# Map输出的处理:创建分区器
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 构造 MapOutputBuffer 对象
// Class<?>[] collectorClasses = job.getClasses(
// JobContext.MAP_OUTPUT_COLLECTOR_CLASS_ATTR, MapOutputBuffer.class);
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
// 有多少个reduce任务,就有多少个分区
partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {
// 创建多分区的分区器,默认:Partitioner.class
// 可通过job.setPartitionerClass(clc.class);进行干预;
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {
// 创建单分区的分区器为0
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
}
// 获取分区器对象
public Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>> getPartitionerClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 默认分区器:HashPartitioner
return (Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR, HashPartitioner.class);
}
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
// HashPartitioner分区器:
// 计算分区个数:key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE得到一个非负的整数 模上 reduce 任务的个数
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
# Map输出的缓冲区初始化:MapOutputBuffer.init
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks
// 溢写的阈值,默认0.8
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
// 缓冲区总大小,默认100M
final int sortmb = job.getInt(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB, 100);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
// 排序器,默认快排:QuickSort.class
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass("map.sort.class",
QuickSort.class, IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb);
LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit);
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec);
// k/v serialization
// 获取比较器,默认:Map输出的Key类型自身的比较器
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
// 获取map输出的key的类型
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
// 获取map输出的value的类型
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
// 序列化key、value进行输出
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
// combiner 优化器(也是一个比例问题(优化前和优化后的记录条数比),达到一定的比例,才会进行优化)
// 对map进行自身数据的reduce处理,可以减少io传输
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
// 把溢写的小文件合并成一个大文件,默认:3。当溢写次数超过了这个值,会触发合并的combinerRunner
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
// 溢写线程(排序,combiner、溢写)(combiner是在溢写的线程中执行的)
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}
# Map输出的处理:SpillThread溢写线程
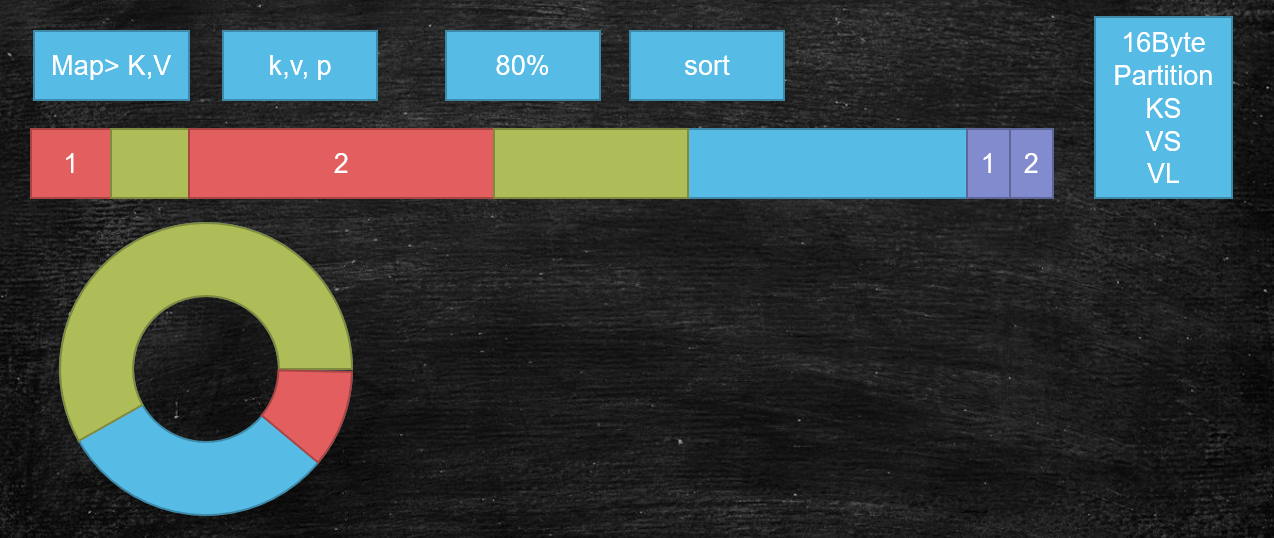
// 溢写线程
protected class SpillThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
spillLock.lock();
spillThreadRunning = true;
try {
while (true) {
spillDone.signal();
while (!spillInProgress) {
spillReady.await();
}
try {
spillLock.unlock();
sortAndSpill();
} catch (Throwable t) {
sortSpillException = t;
} finally {
spillLock.lock();
if (bufend < bufstart) {
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
}
kvstart = kvend;
bufstart = bufend;
spillInProgress = false;
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
spillThreadRunning = false;
}
}
}
// 排序并溢写
private void sortAndSpill() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
//approximate the length of the output file to be the length of the
//buffer + header lengths for the partitions
final long size = distanceTo(bufstart, bufend, bufvoid) +
partitions * APPROX_HEADER_LENGTH;
FSDataOutputStream out = null;
try {
// create spill file
final SpillRecord spillRec = new SpillRecord(partitions);
final Path filename =
mapOutputFile.getSpillFileForWrite(numSpills, size);
out = rfs.create(filename);
final int mstart = kvend / NMETA;
final int mend = 1 + // kvend is a valid record
(kvstart >= kvend
? kvstart
: kvmeta.capacity() + kvstart) / NMETA;
sorter.sort(MapOutputBuffer.this, mstart, mend, reporter);
int spindex = mstart;
final IndexRecord rec = new IndexRecord();
final InMemValBytes value = new InMemValBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < partitions; ++i) {
IFile.Writer<K, V> writer = null;
try {
long segmentStart = out.getPos();
FSDataOutputStream partitionOut = CryptoUtils.wrapIfNecessary(job, out);
writer = new Writer<K, V>(job, partitionOut, keyClass, valClass, codec,
spilledRecordsCounter);
// 溢写过程中调用 combiner 优化器
if (combinerRunner == null) {
// spill directly
DataInputBuffer key = new DataInputBuffer();
while (spindex < mend &&
kvmeta.get(offsetFor(spindex % maxRec) + PARTITION) == i) {
final int kvoff = offsetFor(spindex % maxRec);
int keystart = kvmeta.get(kvoff + KEYSTART);
int valstart = kvmeta.get(kvoff + VALSTART);
key.reset(kvbuffer, keystart, valstart - keystart);
getVBytesForOffset(kvoff, value);
writer.append(key, value);
++spindex;
}
} else {
int spstart = spindex;
while (spindex < mend &&
kvmeta.get(offsetFor(spindex % maxRec)
+ PARTITION) == i) {
++spindex;
}
// Note: we would like to avoid the combiner if we've fewer
// than some threshold of records for a partition
if (spstart != spindex) {
combineCollector.setWriter(writer);
RawKeyValueIterator kvIter =
new MRResultIterator(spstart, spindex);
combinerRunner.combine(kvIter, combineCollector);
}
}
// close the writer
writer.close();
// record offsets
rec.startOffset = segmentStart;
rec.rawLength = writer.getRawLength() + CryptoUtils.cryptoPadding(job);
rec.partLength = writer.getCompressedLength() + CryptoUtils.cryptoPadding(job);
spillRec.putIndex(rec, i);
writer = null;
} finally {
if (null != writer) writer.close();
}
}
if (totalIndexCacheMemory >= indexCacheMemoryLimit) {
// create spill index file
Path indexFilename =
mapOutputFile.getSpillIndexFileForWrite(numSpills, partitions
* MAP_OUTPUT_INDEX_RECORD_LENGTH);
spillRec.writeToFile(indexFilename, job);
} else {
indexCacheList.add(spillRec);
totalIndexCacheMemory +=
spillRec.size() * MAP_OUTPUT_INDEX_RECORD_LENGTH;
}
LOG.info("Finished spill " + numSpills);
++numSpills;
} finally {
if (out != null) out.close();
}
}
# Map输出的处理:context.write(key, value);
// WrappedMapper 的 write方法
@Override
public void write(KEYOUT key, VALUEOUT value) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
mapContext.write(key, value);
}
// MapContextImpl 父类 TaskInputOutputContextImpl 的 write方法
/**
* Generate an output key/value pair.
*/
public void write(KEYOUT key, VALUEOUT value
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
output.write(key, value);
}
// NewOutputCollector 的 write方法
@Override
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// key value partition
collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
}
# Map输出的缓冲区:MapOutputBuffer
/**
* Serialize the key, value to intermediate storage.
* When this method returns, kvindex must refer to sufficient unused
* storage to store one METADATA.
*/
// key value partition
public synchronized void collect(K key, V value, final int partition
) throws IOException {
reporter.progress();
if (key.getClass() != keyClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in key from map: expected "
+ keyClass.getName() + ", received "
+ key.getClass().getName());
}
if (value.getClass() != valClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in value from map: expected "
+ valClass.getName() + ", received "
+ value.getClass().getName());
}
if (partition < 0 || partition >= partitions) {
throw new IOException("Illegal partition for " + key + " (" +
partition + ")");
}
checkSpillException();
bufferRemaining -= METASIZE;
if (bufferRemaining <= 0) {
// start spill if the thread is not running and the soft limit has been
// reached
spillLock.lock();
try {
do {
if (!spillInProgress) {
final int kvbidx = 4 * kvindex;
final int kvbend = 4 * kvend;
// serialized, unspilled bytes always lie between kvindex and
// bufindex, crossing the equator. Note that any void space
// created by a reset must be included in "used" bytes
final int bUsed = distanceTo(kvbidx, bufindex);
final boolean bufsoftlimit = bUsed >= softLimit;
if ((kvbend + METASIZE) % kvbuffer.length !=
equator - (equator % METASIZE)) {
// spill finished, reclaim space
resetSpill();
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx) - 2 * METASIZE,
softLimit - bUsed) - METASIZE;
continue;
} else if (bufsoftlimit && kvindex != kvend) {
// spill records, if any collected; check latter, as it may
// be possible for metadata alignment to hit spill pcnt
startSpill();
final int avgRec = (int)
(mapOutputByteCounter.getCounter() /
mapOutputRecordCounter.getCounter());
// leave at least half the split buffer for serialization data
// ensure that kvindex >= bufindex
final int distkvim= distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx);
final int newPos = (bufindex +
Math.max(2 * METASIZE - 1,
Math.min(distkvim/ 2,
distkvim/ (METASIZE + avgRec) * METASIZE)))
% kvbuffer.length;
setEquator(newPos);
bufmark = bufindex = newPos;
final int serBound = 4 * kvend;
// bytes remaining before the lock must be held and limits
// checked is the minimum of three arcs: the metadata space, the
// serialization space, and the soft limit
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
// metadata max
distanceTo(bufend, newPos),
Math.min(
// serialization max
distanceTo(newPos, serBound),
// soft limit
softLimit)) - 2 * METASIZE;
}
}
} while (false);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
}
try {
// 序列化 key bytes into buffer
int keystart = bufindex;
keySerializer.serialize(key);
if (bufindex < keystart) {
// wrapped the key; must make contiguous
bb.shiftBufferedKey();
keystart = 0;
}
// 序列化 value bytes into buffer
final int valstart = bufindex;
valSerializer.serialize(value);
// It's possible for records to have zero length, i.e. the serializer
// will perform no writes. To ensure that the boundary conditions are
// checked and that the kvindex invariant is maintained, perform a
// zero-length write into the buffer. The logic monitoring this could be
// moved into collect, but this is cleaner and inexpensive. For now, it
// is acceptable.
bb.write(b0, 0, 0);
// the record must be marked after the preceding write, as the metadata
// for this record are not yet written
int valend = bb.markRecord();
mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1);
mapOutputByteCounter.increment(
distanceTo(keystart, valend, bufvoid));
// write accounting info
kvmeta.put(kvindex + PARTITION, partition);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + KEYSTART, keystart);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALSTART, valstart);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALLEN, distanceTo(valstart, valend));
// advance kvindex
kvindex = (kvindex - NMETA + kvmeta.capacity()) % kvmeta.capacity();
} catch (MapBufferTooSmallException e) {
LOG.info("Record too large for in-memory buffer: " + e.getMessage());
spillSingleRecord(key, value, partition);
mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1);
return;
}
}
# ReduceTask源码分析
ReduceTask input -> reduce -> output map:run: while (context.nextKeyValue()) 一条记录调用一次map reduce:run: while (context.nextKey()) 一组数据调用一次reduce doc: 1,shuffle: 洗牌(相同的key被拉取到一个分区),拉取数据 2,sort: 整个MR框架中只有map端是无序到有序的过程,用的是快速排序 reduce这里的所谓的sort其实 你可以想成就是一个对着map排好序的一堆小文件做归并排序 grouping comparator 1970-1-22 33 bj 1970-1-8 23 sh 排序比较啥:年,月,温度,,且温度倒序 分组比较器:年,月 3,reduce: run: rIter = shuffle。。//reduce拉取回属于自己的数据,并包装成迭代器~!真@迭代器 file(磁盘上)-> open -> readline -> hasNext() next() 时时刻刻想:我们做的是大数据计算,数据可能撑爆内存~! comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator(); 1,取用户设置的分组比较器 2,取getOutputKeyComparator(); 1,优先取用户覆盖的自定义排序比较器 2,保底,取key这个类型自身的比较器 #:分组比较器可不可以复用排序比较器 什么叫做排序比较器:返回值:-1,0,1 什么叫做分组比较器:返回值:布尔值,false/true 排序比较器可不可以做分组比较器:可以的 mapTask reduceTask 1. 取用户自定义的分组比较器 1. 用户定义的排序比较器 2. 用户定义的排序比较器 2. 取key 自身的排序比较器 3. 取key自身的排序比较器 组合方式: 1)不设置排序和分组比较器: map:取key自身的排序比较器 reduce:取key自身的排序比较器 2)设置了排序 map:用户定义的排序比较器 reduce:用户定义的排序比较器 3)设置了分组 map:取key自身的排序比较器 reduce:取用户自定义的分组比较器 4)设置了排序和分组 map:用户定义的排序比较器 reduce:取用户自定义的分组比较器 做减法:结论,框架很灵活,给了我们各种加工数据排序和分组的方式 ReduceContextImpl input = rIter 真@迭代器 hasMore = true nextKeyIsSame = false iterable = ValueIterable iterator = ValueIterator ValueIterable iterator() return iterator; ValueIterator 假@迭代器 嵌套迭代器 hasNext() return firstValue || nextKeyIsSame; next() nextKeyValue(); nextKey() nextKeyValue() nextKeyValue() 1,通过input取数据,对key和value赋值 2,返回布尔值 3,多取一条记录判断更新nextKeyIsSame 窥探下一条记录是不是还是一组的! getCurrentKey() return key getValues() return iterable; **: reduceTask拉取回的数据被包装成一个迭代器 reduce方法被调用的时候,并没有把一组数据真的加载到内存 而是传递一个迭代器-values 在reduce方法中使用这个迭代器的时候: hasNext方法判断nextKeyIsSame:下一条是不是还是一组 next方法:负责调取nextKeyValue方法,从reduceTask级别的迭代器中取记录, 并同时更新nextKeyIsSame 以上的设计艺术: 充分利用了迭代器模式: 规避了内存数据OOM的问题 且:之前不是说了框架是排序的 所以真假迭代器他们只需要协作,一次I/O就可以线性处理完每一组数据~!
# Reduce主要流程:
public void run(JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
if (isMapOrReduce()) {
copyPhase = getProgress().addPhase("copy");
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort");
reducePhase = getProgress().addPhase("reduce");
}
// start thread that will handle communication with parent
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewReducer();
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
// Initialize the codec
codec = initCodec();
RawKeyValueIterator rIter = null;
ShuffleConsumerPlugin shuffleConsumerPlugin = null;
Class combinerClass = conf.getCombinerClass();
CombineOutputCollector combineCollector =
(null != combinerClass) ?
new CombineOutputCollector(reduceCombineOutputCounter, reporter, conf) : null;
Class<? extends ShuffleConsumerPlugin> clazz =
job.getClass(MRConfig.SHUFFLE_CONSUMER_PLUGIN, Shuffle.class, ShuffleConsumerPlugin.class);
shuffleConsumerPlugin = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, job);
LOG.info("Using ShuffleConsumerPlugin: " + shuffleConsumerPlugin);
ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context shuffleContext =
new ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context(getTaskID(), job, FileSystem.getLocal(job), umbilical,
super.lDirAlloc, reporter, codec,
combinerClass, combineCollector,
spilledRecordsCounter, reduceCombineInputCounter,
shuffledMapsCounter,
reduceShuffleBytes, failedShuffleCounter,
mergedMapOutputsCounter,
taskStatus, copyPhase, sortPhase, this,
mapOutputFile, localMapFiles);
shuffleConsumerPlugin.init(shuffleContext);
// shuffle拉取数据返回一个真迭代器
rIter = shuffleConsumerPlugin.run();
// free up the data structures
mapOutputFilesOnDisk.clear();
sortPhase.complete(); // sort is complete
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.REDUCE);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
Class keyClass = job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
Class valueClass = job.getMapOutputValueClass();
RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator();
if (useNewApi) {
runNewReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
} else {
runOldReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
}
shuffleConsumerPlugin.close();
done(umbilical, reporter);
}
# 前置参数组装:ReduceTask.runNewReducer();
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewReducer(JobConf job,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
final TaskReporter reporter,
RawKeyValueIterator rIter,
RawComparator<INKEY> comparator,
Class<INKEY> keyClass,
Class<INVALUE> valueClass
) throws IOException,InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
// wrap value iterator to report progress.
final RawKeyValueIterator rawIter = rIter;
rIter = new RawKeyValueIterator() {
public void close() throws IOException {
rawIter.close();
}
public DataInputBuffer getKey() throws IOException {
return rawIter.getKey();
}
public Progress getProgress() {
return rawIter.getProgress();
}
public DataInputBuffer getValue() throws IOException {
return rawIter.getValue();
}
public boolean next() throws IOException {
boolean ret = rawIter.next();
reporter.setProgress(rawIter.getProgress().getProgress());
return ret;
}
};
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(), reporter);
// make a reducer
// 通过反射得到我们自己写的Reduce类对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> reducer =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getReducerClass(), job);
// 输出对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter<OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> trackedRW =
new NewTrackingRecordWriter<OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(this, taskContext);
job.setBoolean("mapred.skip.on", isSkipping());
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
// 包装 reducer、rIter、trackedRW 得到reduce的上下文对象 reducerContext
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer.Context
reducerContext = createReduceContext(reducer, job, getTaskID(),
rIter, reduceInputKeyCounter,
reduceInputValueCounter,
trackedRW,
committer,
reporter, comparator, keyClass,
valueClass);
try {
reducer.run(reducerContext);
} finally {
trackedRW.close(reducerContext);
}
}
# Reduce的context.nextKeyValue()
// 处理下一组key
public boolean nextKey() throws IOException,InterruptedException {
while (hasMore && nextKeyIsSame) {
nextKeyValue();
}
if (hasMore) {
if (inputKeyCounter != null) {
inputKeyCounter.increment(1);
}
return nextKeyValue();
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 调用迭代器的相关方法
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (!hasMore) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
}
firstValue = !nextKeyIsSame;
DataInputBuffer nextKey = input.getKey();
currentRawKey.set(nextKey.getData(), nextKey.getPosition(),
nextKey.getLength() - nextKey.getPosition());
buffer.reset(currentRawKey.getBytes(), 0, currentRawKey.getLength());
key = keyDeserializer.deserialize(key);
DataInputBuffer nextVal = input.getValue();
buffer.reset(nextVal.getData(), nextVal.getPosition(), nextVal.getLength()
- nextVal.getPosition());
value = valueDeserializer.deserialize(value);
currentKeyLength = nextKey.getLength() - nextKey.getPosition();
currentValueLength = nextVal.getLength() - nextVal.getPosition();
if (isMarked) {
backupStore.write(nextKey, nextVal);
}
// 窥探下一条记录是不是还是一组的!
hasMore = input.next();
if (hasMore) {
nextKey = input.getKey();
// 多取一条记录判断更新 nextKeyIsSame
nextKeyIsSame = comparator.compare(currentRawKey.getBytes(), 0,
currentRawKey.getLength(),
nextKey.getData(),
nextKey.getPosition(),
nextKey.getLength() - nextKey.getPosition()
) == 0;
} else {
nextKeyIsSame = false;
}
inputValueCounter.increment(1);
return true;
}
# MapReduce的Java实现
# WordCount
# Map
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class HadoopMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
//hadoop框架中,它是一个分布式 数据 :序列化、反序列化
//hadoop有自己一套可以序列化、反序列化
//或者自己开发类型必须:实现序列化,反序列化接口,实现比较器接口
//排序 -》 比较 这个世界有2种顺序: 8 11, 字典序、数值顺序
// value 会被序列化,所以放在外面,可以减少对象的创建,减少gc的发生
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
// key 会被序列化,所以放在外面,可以减少对象的创建,减少gc的发生
private Text word = new Text();
/**
* 对key进行分组
* @param key 是每一行字符串自己第一个字节面向源文件的偏移量
* @param value 每一行的字符串
* @param context 上下文对象
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (stringTokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
# Reduce
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class HadoopReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
/**
* 相同的key为一组 ,这一组数据调用一次reduce
* @param key map阶段的key值
* @param values map阶段的value值
* @param context 上下文对象
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable intWritable : values) {
sum += intWritable.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
# 打成jar包上传到集群环境上
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* 打成jar包上传到集群环境上,在集群上通过 hadoop -jar 运行
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class HadoopWordCountJar {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(HadoopWordCountJar.class);
// 指定job的名称
job.setJobName("tiankafei-wordcount");
// 指定输入文件的路径
Path inFile = new Path("/data/wc/input");
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inFile);
// 指定输出文件的路径
Path outFile = new Path("/data/wc/output");
if (outFile.getFileSystem(conf).exists(outFile)) {
outFile.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outFile, true);
}
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outFile);
// 指定Map处理类
job.setMapperClass(HadoopMapper.class);
// 指定map的输出key类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 指定map的输出value类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 指定reduce处理类
job.setReducerClass(HadoopReduce.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
# 客户端在windows上执行,map,reduce在集群环境上运行
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* 客户端在windows上执行,map,reduce在集群环境上运行
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class HadoopWordCountCluster {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root");
// 让框架知道在windows上执行,需要设置为true
conf.set("mapreduce.app-submission.cross-platform", "true");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
// 把本地jar包上传到hadoop上
job.setJar("E:\\gits\\tiankafei\\tiankafei-code-learn\\scala-project\\target\\scala-project-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar");
job.setJarByClass(HadoopWordCountCluster.class);
// 指定job的名称
job.setJobName("tiankafei-wordcount");
// 指定输入文件的路径
Path inFile = new Path("/data/wc/input");
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inFile);
// 指定输出文件的路径
Path outFile = new Path("/data/wc/output");
if (outFile.getFileSystem(conf).exists(outFile)) {
outFile.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outFile, true);
}
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outFile);
// 指定Map处理类
job.setMapperClass(HadoopMapper.class);
// 指定map的输出key类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 指定map的输出value类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 指定reduce处理类
job.setReducerClass(HadoopReduce.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
# 完全本地执行
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* 客户端在windows上执行,map,reduce也在windows上运行
* 需要配置本地hadoop环境变量,且hadoop的bin目录需要有winutils.exe这个文件
*
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class HadoopWordCountLocal {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root");
// 让框架知道在windows上执行,需要设置为true
conf.set("mapreduce.app-submission.cross-platform", "true");
// 让框架在本地运行
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name", "local");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(HadoopWordCountLocal.class);
// 指定job的名称
job.setJobName("tiankafei-wordcount");
// 指定输入文件的路径
Path inFile = new Path("/data/wc/input");
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inFile);
// 指定输出文件的路径
Path outFile = new Path("/data/wc/output");
if (outFile.getFileSystem(conf).exists(outFile)) {
outFile.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outFile, true);
}
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outFile);
// 指定Map处理类
job.setMapperClass(HadoopMapper.class);
// 指定map的输出key类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// 指定map的输出value类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 指定reduce处理类
job.setReducerClass(HadoopReduce.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
# TopN
数据集可能有几百G,甚至几T的数据,
要求:获取每月温度最高的两天
2019-6-1 22:22:22 1 39
2019-5-21 22:22:22 3 33
2019-6-1 22:22:22 1 38
2019-6-2 22:22:22 2 31
2018-3-11 22:22:22 3 18
2018-4-23 22:22:22 1 22
1970-8-23 22:22:22 2 23
1970-8-8 22:22:22 1 32
# 运行主类
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root");
// 让框架知道在windows上执行,需要设置为true
conf.set("mapreduce.app-submission.cross-platform", "true");
// 让框架在本地运行
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name", "local");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(TopNRunner.class);
// 指定job的名称
job.setJobName("tiankafei-topn");
// 指定输入文件的路径
Path inFile = new Path("/data/topn/input");
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inFile);
// 指定输出文件的路径
Path outFile = new Path("/data/topn/output");
if (outFile.getFileSystem(conf).exists(outFile)) {
outFile.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outFile, true);
}
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outFile);
// mapper
job.setMapperClass(TopNMapper.class);
// 自定义分区器
job.setPartitionerClass(TopNPartitioner.class);
// 自定义mapper的key类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(TopNKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 自定义mapper端的排序
job.setSortComparatorClass(TopNSortComparator.class);
// combine job.setCombinerClass();
// 自定义reduce端的排序
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(TopNGroupingComparator.class);
// reduce
job.setReducerClass(TopNReduce.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
# Mapper的Key
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 使用默认通用的排序比较器:按照年月日正序
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class TopNKey implements WritableComparable<TopNKey> {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int wd;
@Override
public int compareTo(TopNKey that) {
int c1 = Integer.compare(this.year, that.getYear());
if(c1 == 0){
int c2 = Integer.compare(this.month, that.getMonth());
if(c2 == 0){
return Integer.compare(this.day, that.getDay());
}
}
return c1;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(this.year);
out.writeInt(this.month);
out.writeInt(this.day);
out.writeInt(this.wd);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.year = in.readInt();
this.month = in.readInt();
this.day = in.readInt();
this.wd = in.readInt();
}
}
# Mapper
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, TopNKey, IntWritable> {
private TopNKey mapKey = new TopNKey();
private IntWritable mapValue = new IntWritable();
private SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 2019-6-1 22:22:22 1 39
String[] arr = StringUtils.split(value.toString(), '\t');
try {
Date date = formatter.parse(arr[0]);
calendar.setTime(date);
int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int monthValue = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
int dayOfMonth = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
int wd = Integer.valueOf(arr[2]);
mapKey.setYear(year).setMonth(monthValue).setDay(dayOfMonth).setWd(wd);
mapValue.set(wd);
context.write(mapKey, mapValue);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
# Mapper分区器
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
/**
* 按照年月进行分区,年月会拉到一个组里
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNPartitioner extends Partitioner<TopNKey, IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(TopNKey topNKey, IntWritable intWritable, int numPartitions) {
return (topNKey.getYear() + topNKey.getMonth()) % numPartitions;
}
}
# Mapper的排序器
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
/**
* map端排序:按照年月正序,温度倒序,减少reduce端IO的拉取
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNSortComparator extends WritableComparator {
public TopNSortComparator() {
super(TopNKey.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
TopNKey k1 = (TopNKey) a;
TopNKey k2 = (TopNKey) b;
int c1 = Integer.compare(k1.getYear(), k2.getYear());
if(c1 == 0){
int c2 = Integer.compare(k1.getMonth(), k2.getMonth());
if(c2 == 0){
return -Integer.compare(k1.getWd(), k2.getWd());
}
return c2;
}
return c1;
}
}
# Reduce
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNReduce extends Reducer<TopNKey, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private Text reduceKey = new Text();
private IntWritable reduceValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(TopNKey key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 因为是按照年月进行的分区,故每次迭代value,key会跟着发生变化;如果是根据key进行分区的,则值不会变化
int index = 0;
int dayFlag = 0;
Iterator<IntWritable> iterator = values.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
IntWritable next = iterator.next();
int year = key.getYear();
int month = key.getMonth();
int day = key.getDay();
int wd = key.getWd();
if(index == 0){
reduceKey.set(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
reduceValue.set(wd);
context.write(reduceKey, reduceValue);
dayFlag = day;
}
if(index != 0 && dayFlag != day){
reduceKey.set(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
reduceValue.set(wd);
context.write(reduceKey, reduceValue);
break;
}
index++;
}
}
}
# Reduce的排序器
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.topn;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
/**
* reduce端按照年月分组排序
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TopNGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
public TopNGroupingComparator() {
super(TopNKey.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
TopNKey k1 = (TopNKey) a;
TopNKey k2 = (TopNKey) b;
int c1 = Integer.compare(k1.getYear(), k2.getYear());
if(c1 == 0){
int c2 = Integer.compare(k1.getMonth(), k2.getMonth());
return c2;
}
return c1;
}
}
# Mapper端的Join操作
# 运行主类需要修改的内容
// 去掉让框架在本地运行的配置
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name", "local");
// 把本地jar包上传到hadoop上
job.setJar("jar包路径");
job.addCacheFile(new Path("/data/topn/dict/dict.txt").toUri());
# Key
// 增加属性
private String location;
// 属性增加序列化
out.writeUTF(this.location);
// 属性增加反序列化
this.location = in.readUTF();
# Mapper增加逻辑代码
private Map<String, String> dictMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
Path path = new Path(cacheFiles[0].getPath());
FileReader fileReader = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(new File(path.getName()));
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String line = null;
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
String[] split = StringUtils.split(line, '\t');
dictMap.put(split[0], split[1]);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fileReader != null){
fileReader.close();
}
if(bufferedReader != null){
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
}
// 并给key赋值
mapKey.setLocation(dictMap.get("代码"))
# Reduce增加输出
reduceKey.set(year + "-" + month + "-" + day + "----" + key.getLocation());
reduceValue.set(wd);
context.write(reduceKey, reduceValue);
# 大数据思维模式
大数据推荐好友:只能推荐陌生人
好友列表:
好友1 好友2 好友3 好友4 好友2 好友1 好友3 好友3 好友1 好友2 好友5 好友6 好友4 好友1 好友5 好友5 好友3 好友4 好友6 好友3 好友7 好友7 好友6
# 运行主类
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.thinking;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class ThinkingRunnerLocal {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(true);
System.setProperty("HADOOP_USER_NAME", "root");
// 让框架知道在windows上执行,需要设置为true
conf.set("mapreduce.app-submission.cross-platform", "true");
// 让框架在本地运行
conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name", "local");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(ThinkingRunnerLocal.class);
// 指定job的名称
job.setJobName("tiankafei-fof");
// 指定输入文件的路径
Path inFile = new Path("/data/fof/input");
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job, inFile);
// 指定输出文件的路径
Path outFile = new Path("/data/fof/output");
if (outFile.getFileSystem(conf).exists(outFile)) {
outFile.getFileSystem(conf).delete(outFile, true);
}
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outFile);
// mapper
job.setMapperClass(ThinkingMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// reduce
job.setReducerClass(ThinkingReduce.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
# Mapper
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.thinking;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.StringUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class ThinkingMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private Text mapKey = new Text();
private IntWritable mapValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 好友1 好友2 好友3 好友4
String[] arr = StringUtils.split(value.toString(), ' ');
for (int i = 0, length = arr.length; i < length; i++) {
String v1 = arr[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
String v2 = arr[j];
String key1 = "";
int c1 = v1.compareTo(v2);
if(c1 > 0){
key1 = v1 + " " + v2;
}else{
key1 = v2 + " " + v1;
}
if(i == 0){
// 直接好友是0
mapKey.set(key1);
mapValue.set(0);
context.write(mapKey, mapValue);
}else{
// 间接好友是1
mapKey.set(key1);
mapValue.set(1);
context.write(mapKey, mapValue);
}
}
}
}
}
# Reduce
package cn.tiankafei.bigdata.hadoop.thinking;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @author tiankafei
* @since 1.0
**/
public class ThinkingReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable reduceValue = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
Iterator<IntWritable> iterator = values.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
IntWritable next = iterator.next();
int v = next.get();
if(v == 0){
// 如果是直接好友,则直接跳出
break;
}
// 间接好友+1,数值越大,共同好友越多
sum += v;
}
if(sum != 0){
// 只输出间接好友
reduceValue.set(sum);
context.write(key, reduceValue);
}
}
}